Pros and Cons of Laser Surgery for Glaucoma
Understanding Glaucoma
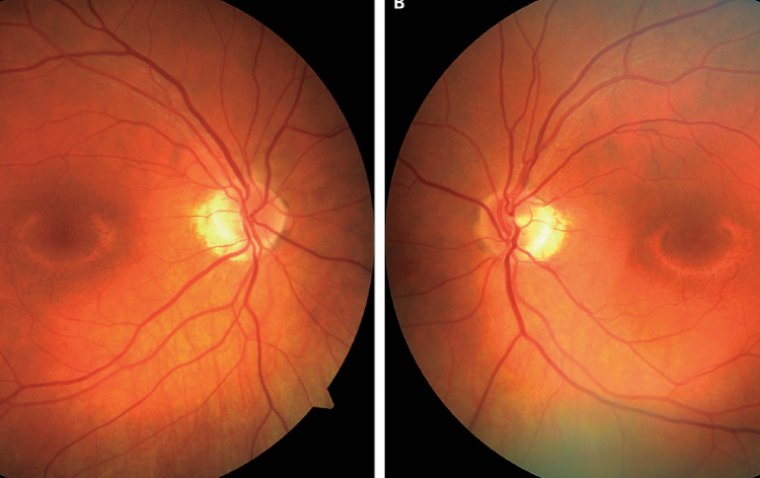
Glaucoma is a complex eye condition characterized by increased intraocular pressure, which can lead to damage to the optic nerve and vision loss if left untreated. This group of eye disorders often develops without noticeable symptoms in its early stages, earning it the nickname "the silent thief of sight." Glaucoma primarily affects peripheral vision, gradually reducing the field of view, and can ultimately lead to blindness if not managed effectively. Early detection and treatment are vital to slow the progression of this condition, making regular eye examinations crucial, especially for individuals at higher risk.
Laser Surgery Overview
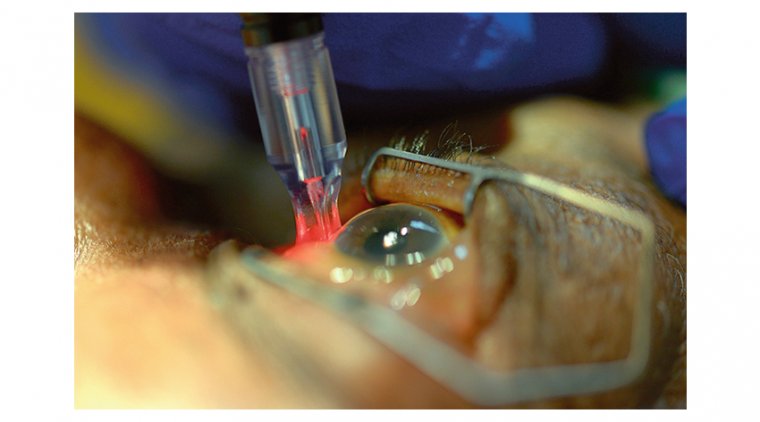
Laser surgery is an innovative and minimally invasive treatment option for glaucoma. It involves the use of a specialized laser to lower intraocular pressure (IOP) in the eye, which is the primary goal in glaucoma management. This surgical approach is typically recommended when medications or other conventional treatments fail to adequately control IOP.
Laser surgery for glaucoma comes in various forms, including Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) and Laser Peripheral Iridotomy (LPI), among others. These procedures are designed to enhance the outflow of aqueous humor (the clear fluid inside the eye) and reduce pressure on the optic nerve.
Unlike traditional glaucoma surgeries, laser procedures are less invasive and often performed on an outpatient basis. They typically offer quicker recovery times and fewer complications, making them a valuable option in the management of this sight-threatening condition. However, like any medical procedure, laser surgery for glaucoma has its pros and cons, which should be carefully considered.
The Pros of Laser Surgery for Glaucoma
Laser surgery for glaucoma offers several notable advantages, making it a preferred choice for many patients and eye care specialists:
1. Effective Reduction of Intraocular Pressure (IOP): The primary goal of glaucoma treatment is to lower intraocular pressure, as high IOP is a significant risk factor for the disease. Laser surgery, such as Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT), can effectively lower IOP, often reducing or eliminating the need for glaucoma medications.
2. Minimally Invasive: Laser procedures are minimally invasive compared to traditional glaucoma surgeries like trabeculectomy or drainage implant surgery. This means less tissue disruption, reduced surgical trauma, and typically quicker recovery times.
3. Outpatient Procedure: Laser surgery is often performed on an outpatient basis, meaning patients can return home the same day. This eliminates the need for an overnight hospital stay.
4. Quick Recovery: Patients typically experience a faster recovery after laser surgery compared to more invasive procedures. There is often minimal post-operative discomfort, and most individuals can resume their regular activities within a short time.
5. Reduced Medication Dependency: Successful laser surgery can reduce or eliminate the need for glaucoma medications, which can have side effects and require strict adherence.
6. Long-Lasting Effects: Depending on the type of laser surgery, the effects can be long-lasting, providing extended relief from elevated IOP.
7. Lower Risk of Complications: Laser procedures generally have a lower risk of complications compared to traditional surgeries, such as infections or scarring.
The Cons of Laser Surgery for Glaucoma
While laser surgery for glaucoma offers several benefits, it's essential to consider the potential drawbacks and risks associated with these procedures:
1. Temporary Pressure Spikes: Following laser surgery, some patients may experience a temporary increase in intraocular pressure (IOP). This pressure spike can be managed with medication, but it's crucial to monitor the IOP closely in the post-operative period.
2. Need for Repeat Procedures: Laser surgery may not provide a permanent solution for all patients. In some cases, the effects of laser treatment may wear off over time, necessitating repeat procedures or the eventual use of other glaucoma treatments.
3. Limited Efficacy in Advanced Cases: Laser surgery is generally most effective in the early to moderate stages of glaucoma. In advanced cases, where extensive damage to the optic nerve has occurred, laser treatment may have limited efficacy, and more invasive surgical options might be necessary.
4. Potential Side Effects: Although relatively rare, laser surgery can have side effects. These may include transient eye discomfort, inflammation, and, in very rare cases, damage to other eye structures.
5. Not Suitable for All Glaucoma Types: Laser surgery is most effective for open-angle glaucoma, where there is a problem with the eye's drainage system. It may not be suitable for other types of glaucoma, such as angle-closure or congenital glaucoma.
6. Cost Considerations: Depending on the specific type of laser surgery and geographic location, the cost of the procedure can be a factor. Insurance coverage may vary, so patients should check their policy and discuss financial aspects with their healthcare provider.
7. Need for Ongoing Monitoring: Even after successful laser surgery, glaucoma patients require ongoing monitoring and follow-up appointments to assess the treatment's effectiveness and adjust management if necessary.
Comparison with Other Treatments
Laser surgery for glaucoma offers several advantages and disadvantages when compared to other glaucoma treatment options like medication and traditional surgery.
Medication
● Pros: Glaucoma medications can effectively lower intraocular pressure and are often the first-line treatment. They are generally non-invasive and don't require surgery.
● Cons: Medications may have side effects, require strict adherence, and can be costly over time. Some patients may be intolerant or allergic to specific medications.
Traditional Surgery (Trabeculectomy)
● Pros: Traditional surgery can provide long-lasting pressure reduction, making it effective for advanced glaucoma cases. It may also be suitable for patients who don't respond well to medications or laser surgery.
● Cons: It's a more invasive procedure with a longer recovery time and a higher risk of complications, including infection and scarring. It may not be suitable for all patients, especially those with certain medical conditions.
Who Is Suitable for Laser Surgery?
Patients suitable for laser surgery as a treatment for glaucoma typically meet certain eligibility criteria. While these criteria can vary depending on the specific type of laser surgery, some common factors make a patient a suitable candidate:
1. Diagnosis of Glaucoma: The patient must have been diagnosed with glaucoma and have elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) that requires treatment. Laser surgery is primarily used to lower IOP.
2. Open-Angle Glaucoma: Laser surgery is most effective for open-angle glaucoma, which is the most common form of the condition. Other types of glaucoma may require different treatments.
3. Uncontrolled IOP: Patients with uncontrolled or inadequately controlled IOP on glaucoma medications may be considered for laser surgery. It is often used when medications alone are insufficient.
4. Overall Eye Health: The patient's overall eye health, aside from glaucoma, is a crucial consideration. The eye should be free from other significant eye diseases or conditions that could interfere with the success of laser surgery.
5. Realistic Expectations: Patients must have realistic expectations about the outcomes of laser surgery. While it can be effective at lowering IOP, it may not completely eliminate the need for medication or future treatments.
6. Willingness to Follow Post-Operative Instructions: Patients should be willing and able to follow the post-operative instructions provided by their ophthalmologist. This may include using prescribed eye drops, attending follow-up appointments, and avoiding certain activities during the recovery period.
7. No Contradictory Health Conditions: Certain health conditions or medications may contraindicate laser surgery. Patients should inform their ophthalmologist about their complete medical history and any medications they are taking.
8. No Allergies to Anesthetics or Laser Components: Patients should not have known allergies to the anesthetics or materials used during laser surgery.
Preparation and Recovery
Before Laser Surgery for Glaucoma
Prior to laser surgery, patients will typically have a comprehensive eye examination conducted by their ophthalmologist. This examination helps determine the suitability of the patient for the procedure and assesses the severity of their glaucoma. Patients may be asked to discontinue certain eye drops or medications before the surgery, as these can affect the procedure's effectiveness.
During Laser Surgery for Glaucoma
Laser surgery for glaucoma is typically an outpatient procedure performed in the ophthalmologist's office or an outpatient surgical center. It's generally well-tolerated and doesn't require general anesthesia, although numbing eye drops may be used to ensure patient comfort. During the procedure, the patient's head will be positioned, and a special lens may be placed on the eye to help focus the laser accurately. The ophthalmologist will then use the laser to make small, precise openings or treatments within the eye's drainage system.
After Laser Surgery for Glaucoma
Recovery following laser surgery for glaucoma is relatively quick and straightforward. Patients may experience some mild discomfort or irritation in the treated eye immediately after the procedure, but this typically subsides within a few hours. It's important to have someone accompany the patient to and from the procedure, as their vision may be temporarily affected.
Patients may be prescribed medicated eye drops to reduce inflammation and prevent infection. It's essential to adhere to the prescribed post-operative eye drop regimen and attend any scheduled follow-up appointments with the ophthalmologist. Most patients can resume their regular activities within a day or two, although strenuous exercise and swimming should be avoided for a short time.
Patients should be aware that the full benefits of laser surgery for glaucoma may take several weeks to become apparent, as it may take time for the eye's drainage system to respond to the treatment and lower intraocular pressure. During the recovery period, it's crucial to monitor any changes in vision or unusual symptoms and promptly report them to the ophthalmologist. Additionally, patients should continue to attend regular follow-up appointments to ensure that their glaucoma is effectively managed.
Summary
In summary, laser surgery for glaucoma offers several advantages, including its ability to effectively lower intraocular pressure, its minimally invasive nature, and the relatively rapid recovery it offers. However, there are some cons to consider, such as the possibility of temporary pressure spikes and the potential need for repeat treatments. When compared to alternative glaucoma treatments like medications or traditional surgery, laser surgery can be an excellent choice for certain patients, particularly those with open-angle glaucoma who are looking for a less invasive option. However, suitability for laser surgery depends on individual factors, and patients should consult with their ophthalmologist to determine the best course of action.
Preparing for the procedure involves a comprehensive eye examination and temporarily discontinuing certain medications. During the procedure, patients can expect to be in and out of the doctor's office within an hour, with minimal discomfort. The recovery period is generally short, with most patients resuming normal activities within a day or two. However, the full benefits may take a few weeks to manifest. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the procedure's effectiveness and manage glaucoma effectively. Overall, laser surgery for glaucoma is a valuable treatment option, but the decision should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider based on individual needs and circumstances.
(1).jpg)