7 Tips on How to Reduce Eye Pressure Effectively and Instantly
What Is Intraocular Pressure?
Eye pressure, also known as intraocular pressure (IOP), is a critical factor in maintaining the health of your eyes. Elevated eye pressure can lead to various eye conditions, including glaucoma, which can result in permanent vision loss if left untreated.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of eye pressure, its underlying causes, and effective strategies to reduce and manage it for optimal ocular health.
So What Is Normal Eye Pressure?
Normal eye pressure for adults typically falls within a range of 10 to 21 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). This measurement can vary slightly based on factors such as age, individual variation, and the measurement technique used.
It's important to note that while this range is considered normal for most individuals, some people may have slightly higher or lower eye pressures without any signs of glaucoma or other eye conditions.
The Role of Intraocular Pressure
Intraocular pressure is the fluid pressure within the eye. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the shape of the eye and ensuring proper functioning of the optic nerve and retina. However, excessively high intraocular pressure can damage these structures, leading to vision impairment or loss. This condition is most commonly associated with glaucoma, a group of eye disorders that progressively damage the optic nerve.
Factors Contributing to Elevated Eye Pressure
Several factors contribute to elevated eye pressure:
● Genetics: Family history of glaucoma increases the risk of elevated eye pressure.
● Age: As we age, the risk of developing elevated eye pressure and glaucoma rises.
● Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases can elevate eye pressure.
● Ethnicity: Individuals of African, Hispanic, and Asian descent are at a higher risk of glaucoma.
● Eye Anatomy: Certain eye structures, such as a thinner central cornea or narrow-angle, can predispose individuals to elevated eye pressure.
7 Tips on How to Reduce Eye Pressure
1. Balanced Diet
A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins C and E, omega-3 fatty acids, and zinc can promote healthy eyes and help reduce eye pressure. Incorporate foods like leafy greens, citrus fruits, nuts, and fish into your diet.
What to Eat: Incorporate leafy greens like spinach and kale, citrus fruits like oranges and lemons, nuts, seeds, and fish such as salmon or mackerel into your meals.
Dietary Supplements: Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil supplements have been shown to support retinal function and may help regulate intraocular pressure. Additionally, supplements containing lutein and zeaxanthin, found naturally in leafy greens, protect the eyes from oxidative stress.
Why It Works: These nutrients strengthen eye tissues, reduce oxidative stress, and promote healthy blood flow to the optic nerve.
Adding superfoods like blueberries, carrots, and avocados to your diet can further support eye health
2. Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise improves blood circulation, which can help regulate eye pressure. Activities like brisk walking, swimming, and yoga are beneficial.
Recommended Exercises: Low-impact activities such as brisk walking, swimming, and yoga can effectively regulate IOP.
Special Consideration: Avoid intense activities like heavy lifting or exercises that involve head-down positions, as they may increase eye pressure temporarily.
3. Hydration
Staying adequately hydrated maintains overall eye health and helps regulate eye pressure. Consume sufficient water throughout the day and include hydrating foods like cucumbers and watermelon.
Daily Hydration Tips: Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily, and include hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and celery in your diet.
Avoid Overhydration: Consuming large amounts of water in a short period can temporarily increase eye pressure. Sip water steadily throughout the day.
4. Stress Management
Chronic stress can contribute to elevated eye pressure. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can alleviate stress and promote eye health.
Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness practices into your daily routine.
Yoga for Stress Relief: Eye-friendly yoga poses such as the Child’s Pose or Shavasana can help alleviate both mental stress and eye strain.
5. Screen Time Management
Prolonged screen time can strain your eyes and potentially elevate eye pressure. Follow the 20-20-20 rule – take a 20-second break to look at an object 20 feet away every 20 minutes of screen use. Minimize glare on screens and use blue light filters to reduce strain. Consciously blink to prevent dry eyes, which can exacerbate pressure-related discomfort.
Ergonomic adjustments like proper seating and screen positioning can further reduce strain.
6. Quality Sleep
Prioritize adequate sleep, as it contributes to lower eye pressure. Create a comfortable sleep environment and establish a consistent sleep schedule.
Tips for Better Sleep:
• Maintain a consistent bedtime routine.
• Ensure your sleep environment is dark, quiet, and comfortable.
• void caffeine or screen exposure before bed.
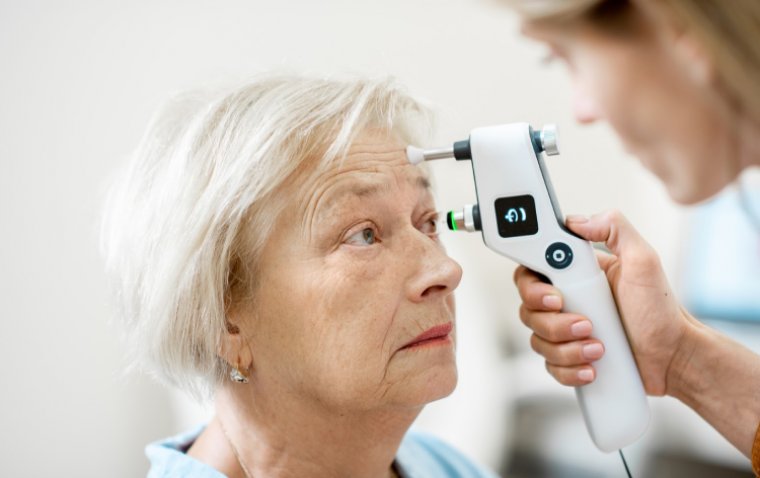
7. Regular Eye Check-ups
Routine eye exams are essential for detecting early signs of elevated eye pressure or other eye conditions. Professionals can measure your eye pressure and offer guidance on managing it effectively.
What to Expect: During an exam, an ophthalmologist will measure your eye pressure using tonometry and assess your optic nerve health.
Frequency: Visit an eye doctor at least once a year, or more frequently if you are at higher risk for elevated IOP.
Quick Relief: How to Reduce Eye Pressure Instantly
1. Blink Regularly
One of the simplest ways to relieve eye pressure is by blinking regularly. Blinking helps spread tear film across the surface of the eye, providing moisture and reducing dryness. Intentional blinking can also help relax your eye muscles and provide immediate relief.
2. Palming
Palming is a relaxation technique that involves covering your closed eyes with your palms, creating a gentle pressure. This method helps block out light and external stimuli, promoting relaxation and reducing strain on the eyes.
How to Do Palming?
1. Sit in a relaxed position.
2. Cover your closed eyes with your palms, ensuring no light enters.
3. Take slow, deep breaths for 1-2 minutes.
3. Eye Massage
Gentle eye massages can help improve blood circulation and alleviate eye pressure. Use your fingertips to apply light pressure around your closed eyelids in a circular motion. Start from the inner corners of your eyes and move outward. Be cautious and avoid pressing too hard.
4. Warm Compress
Applying a warm compress can help relax eye muscles and promote better circulation. Dip a clean cloth in warm water, wring out excess water, and place it over your closed eyelids for a few minutes. The warmth can help ease tension and reduce eye pressure.
5. Cold Compress
Alternatively, a cold compress can also provide relief by reducing inflammation and constricting blood vessels. Use a cold pack or a clean cloth wrapped around ice cubes. Place it gently over your closed eyelids for a minute or two.
6. Focus Shifting
Engage in focus shifting exercises to relieve eye strain and pressure. Choose an object nearby and focus on it for a few seconds, then shift your focus to an object farther away. Repeat this process several times to help relax your eye muscles.
Summary
Maintaining healthy eye pressure is vital for preserving your vision and overall ocular health. By adopting a balanced lifestyle that includes a nutrient-rich diet, regular exercise, stress management, proper hydration, and quality sleep, you can significantly reduce the risk of elevated eye pressure and associated eye conditions like glaucoma. Remember to prioritize regular eye check-ups to catch any issues early and ensure the longevity of your precious eyesight.
(1).jpg)