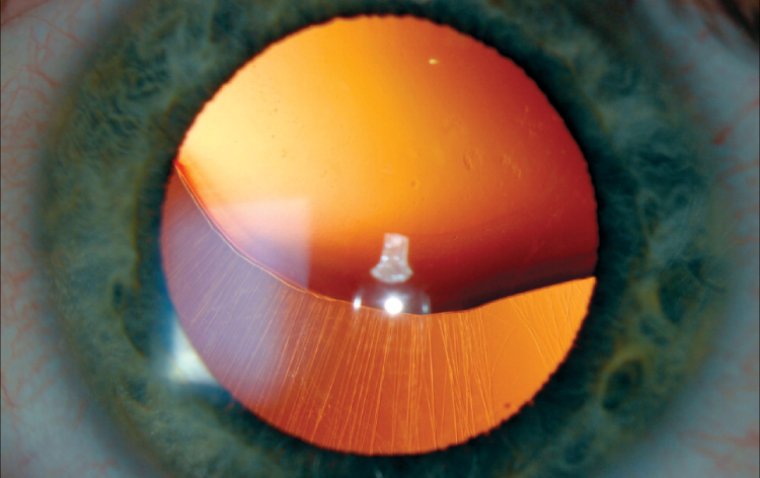
Understanding Ectopia Lentis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Ectopia lentis is a term that holds a pivotal place within the realm of ophthalmology, shedding light on a unique condition that involves the lens of the eye. This condition, characterized by the displacement or dislocation of the lens from its normal position, raises important considerations for both individuals and healthcare professionals.
What Is Ectopia Lentis?
At its core, ectopia lentis refers to a situation where the lens within the eye shifts from its usual position, impacting the way individuals perceive the world around them. The lens, a crucial component responsible for focusing light onto the retina, plays an essential role in clear vision. However, when ectopia lentis occurs, this essential visual apparatus moves, potentially leading to a range of visual disruptions.
Unveiling the Origins: What Causes Ectopia Lentis?
From congenital predispositions to traumatic events, several factors can contribute to this intricate ocular phenomenon. Delving into these causes not only enriches our understanding but also guides diagnosis and treatment strategies.
1. Congenital Conditions:
Several genetic disorders can increase the susceptibility to developing ectopia lentis, a condition characterized by the displacement or dislocation of the eye's lens. These genetic conditions impact the structural integrity and stability of ocular components, contributing to the occurrence of ectopia lentis.
● Marfan syndrome
● Weill–Marchesani syndrome
● Aniridia
● Homocystinuria
● Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
● Pierre Robin syndrome
● Refsum disease
● Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome
● Persistent pupillary membrane
2. Traumatic Events:
● Sudden and severe eye trauma, caused by accidents or injuries, can disrupt the delicate equilibrium of ocular structures, triggering the displacement of the lens.
3. Genetic and Hereditary Factors:
● Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of ectopia lentis are more susceptible due to inherited genetic factors that influence the stability of ocular components.
Common Symptoms of Ectopia Lentis
Credit: Medline Plus
Displacement or dislocation of the lens from its normal position.
● Blurred vision
● Double vision (diplopia)
● Myopia (nearsightedness)
● Red eye
● Photophobia (sensitivity to light)
● Poor vision in bright light or glare
● Eye pain or discomfort
● Abnormal head tilting or squinting to achieve better vision
How to Diagnose Ectopia Lentis
Eye Examinations: The diagnostic process typically commences with a comprehensive eye examination conducted by an ophthalmologist. This involves evaluating the alignment, movement, and structure of the eye components, including the displaced lens.
Visual Acuity Tests: Visual acuity tests assess an individual's ability to perceive visual details at varying distances. These tests help gauge the extent to which lens displacement has affected vision clarity.
Imaging Techniques: Imaging technologies like ultrasound and MRI play a pivotal role in diagnosing ectopia lentis. These techniques provide detailed insights into the position of the lens within the eye and aid in determining the appropriate course of action.
Early diagnosis holds the key to successful management of ectopia lentis. Detecting the condition promptly allows healthcare professionals to initiate targeted interventions that mitigate its impact on visual perception and overall eye health.
Treatment Options: A Multifaceted Approach
1. Non-Surgical Approaches
● Corrective Eyewear: Prescription eyeglasses can compensate for the altered light focusing caused by lens displacement, improving visual clarity and comfort.
● Contact Lenses: Specially designed contact lenses can provide a more precise and adaptable solution for individuals with ectopia lentis.
2. Surgical Interventions
● Lens Repositioning: In cases of partial lens displacement, surgical procedures can be performed to reposition the lens to its natural location, restoring visual acuity.
● Lens Removal: For severe cases or instances where the lens cannot be repositioned effectively, surgical removal (aphakia) may be considered. This involves replacing the lens with an intraocular lens (IOL) implant.
Surgical interventions offer a more permanent solution for ectopia lentis but come with their own set of considerations. While lens repositioning can restore vision, it requires surgical expertise and may carry some risks. Lens removal with IOL implantation can provide clearer vision, but it may necessitate additional follow-up procedures.
How Can I Prevent Ectopia Lentis?
Ectopia lentis is often a genetic condition, meaning it's passed down through families. In some cases, it can be associated with certain connective tissue disorders such as Marfan syndrome and homocystinuria. While there's no surefire way to completely prevent ectopia lentis, there are some steps you can take to reduce the risk or manage the condition:
1. Genetic Counseling: If you have a family history of ectopia lentis or associated conditions, consider genetic counseling. This can help you understand the risks and make informed decisions.
2. Regular Eye Exams: Regular eye exams are crucial for early detection and management of any eye-related issues, including ectopia lentis. Routine check-ups with an ophthalmologist can help identify any potential problems early on.
3. Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have an underlying condition like Marfan syndrome or homocystinuria that is associated with ectopia lentis, it's important to manage that condition with the help of healthcare professionals. Proper management can help mitigate the risk of ectopia lentis and other complications.
4. Protect Your Eyes: Eye injuries can sometimes contribute to the development of ectopia lentis. To minimize the risk of eye injuries, especially in situations where there's a higher risk (e.g., sports, construction work), wearing appropriate protective eyewear is recommended.
5. Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall eye health. This includes a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, staying hydrated, avoiding smoking, and protecting your eyes from excessive sun exposure with sunglasses that provide UV protection.
6. Early Intervention: If you notice any changes in your vision, such as blurriness or discomfort, it's important to seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention and treatment can help prevent the progression of ectopia lentis and associated complications.
7. Compliance with Medical Advice: If you have been diagnosed with ectopia lentis or a related condition, follow your healthcare provider's advice closely. This may involve regular monitoring, medications, or other interventions to manage the condition and prevent complications.
Remember that while these steps can help reduce the risk of ectopia lentis, there's no guaranteed prevention method. Regular communication with healthcare professionals and proactive management of any underlying conditions are essential for maintaining good eye health.
FAQ
Ectopia lentis is often genetic, so prevention may not always be possible. However, managing underlying conditions and maintaining eye health can help reduce the risk.
Yes, depending on the severity, treatment may involve corrective lenses (glasses or contact lenses) to improve vision. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to reposition the lens.
(1).jpg)