Astigmatism: An Overview of Visual Distortion
What Is Astigmatism?
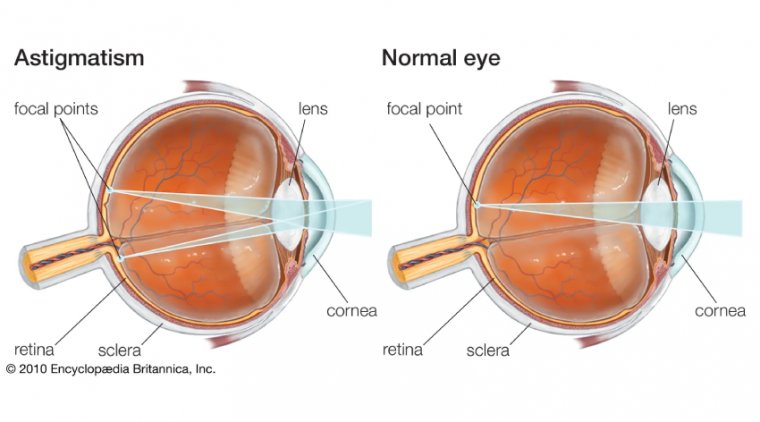
Astigmatism is a common refractive error that causes distorted or blurred vision due to the irregular curvature of the cornea or lens in the eye. The cornea, the transparent front part of the eye, and the lens, a clear structure located behind the iris, work together to refract light and focus it on the retina. In individuals with astigmatism, the light rays do not converge at a single point on the retina, leading to blurry or distorted vision.
Astigmatism affects millions of people worldwide, with some studies estimating that up to one-third of the population experiences some degree of astigmatism. People of all ages can develop astigmatism, but those with a family history of the condition, certain eye conditions, or a history of eye injuries are at a higher risk.
What Causes Astigmatism?
The primary cause of astigmatism is an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, which prevents light from focusing properly on the retina. In a healthy eye, the cornea and lens are smooth and evenly curved, allowing light to focus on a single point on the retina. When the cornea or lens has an irregular shape, light is refracted unevenly, resulting in visual distortion.
Genetics play a significant role in the development of astigmatism. If one or both parents have the condition, their offspring are more likely to develop it. Additionally, certain eye conditions, such as keratoconus or pellucid marginal degeneration, can increase the risk of astigmatism. Eye injuries that alter the shape of the cornea or lens can also lead to astigmatism.
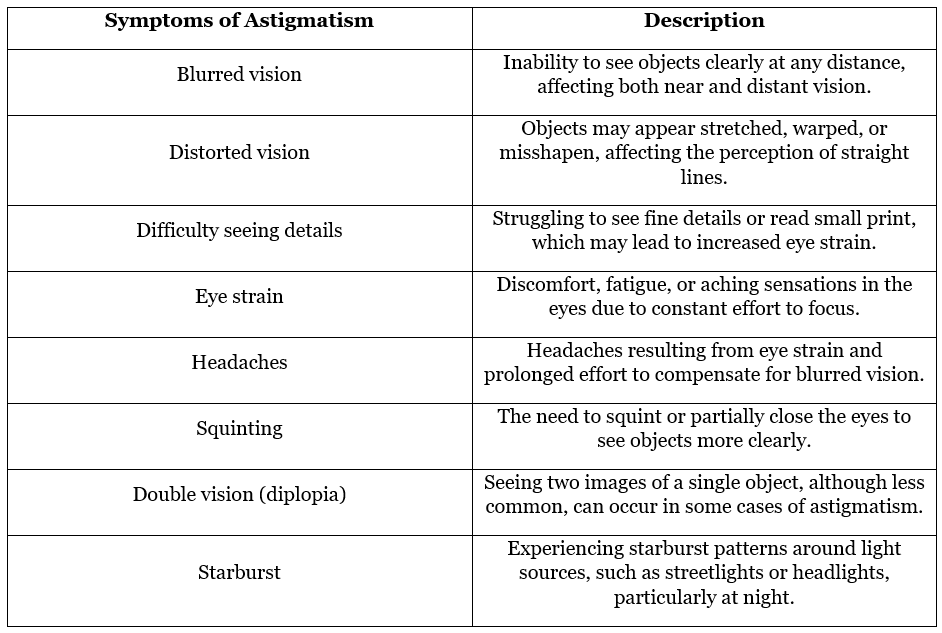
Symptoms of Astigmatism
The primary symptom of astigmatism is blurred or distorted vision at any distance. Individuals with astigmatism may experience difficulty seeing fine details or reading small print, resulting in eye strain and headaches.
Because the eyes are constantly trying to focus and compensate for the irregular curvature, individuals with astigmatism often experience eye strain and headaches, especially after prolonged periods of reading or other close-up work.
Treatment Options for Astigmatism
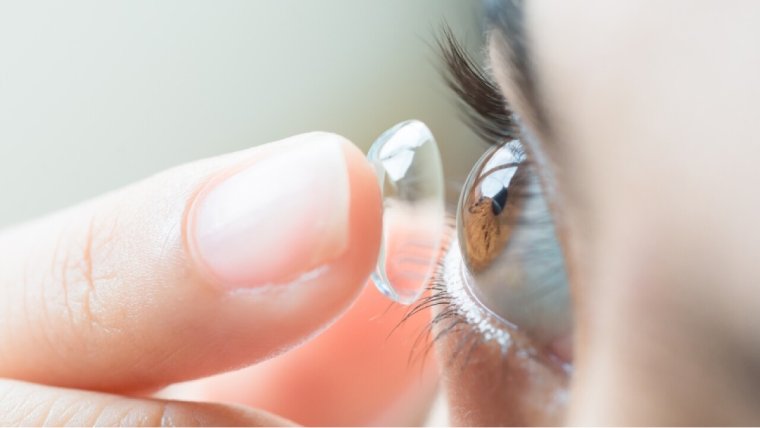
The most common treatment for astigmatism is the use of corrective lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses. These lenses are designed to compensate for the irregular curvature of the cornea or lens, allowing light to focus correctly on the retina.
Refractive surgeries, such as LASIK, PRK, and LASEK, can be effective treatment options for individuals with astigmatism. These procedures reshape the cornea, improving its ability to focus light on the retina and correcting the refractive error.
Alternative methods, such as orthokeratology and photorefractive keratectomy, may also be used to treat astigmatism. Orthokeratology involves wearing specially designed contact lenses that temporarily reshape the cornea, while photorefractive keratectomy uses a laser to remove a small amount of corneal tissue to correct the irregular curvature.
Managing Astigmatism
Regular eye exams are crucial for detecting and managing astigmatism. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the condition from worsening and affecting an individual's quality of life.
Certain lifestyle changes can help individuals with astigmatism manage their symptoms and improve their vision. These may include:
1. Taking regular breaks when engaging in activities that require prolonged focus, such as reading or computer work, to reduce eye strain and fatigue.
2. Adjusting the lighting in your environment to ensure it is comfortable and reduces glare, which can exacerbate symptoms.
3. Practicing good eye hygiene, such as avoiding rubbing your eyes and keeping them clean, to prevent infections and other complications.
4. Ensuring a well-balanced diet with essential nutrients, including vitamins A, C, and E, to support overall eye health.
5. Wearing sunglasses with UV protection to shield your eyes from harmful ultraviolet rays, which can contribute to eye damage and worsen astigmatism.
Conclusion
Astigmatism is a common refractive error caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens, leading to blurred or distorted vision. The condition affects millions of people worldwide and can be managed through various treatment options, including corrective lenses, surgery, and other vision correction methods. If you are experiencing symptoms of astigmatism, such as blurred or distorted vision, eye strain, or headaches, it is crucial to seek professional advice and support. Regular eye exams can help detect astigmatism early, allowing for appropriate management and treatment to prevent the condition from worsening.
In the world of vision, clarity is key. Don't let astigmatism blur your view of life's wonders – seek professional help and unlock your eyes' full potential. Embrace the journey towards visual harmony and let your focus guide you towards a vivid and undistorted future.
(1).jpg)