Blepharoconjunctivitis: A Closer Look at Its Causes and Treatment
What is Blepharoconjunctivitis?
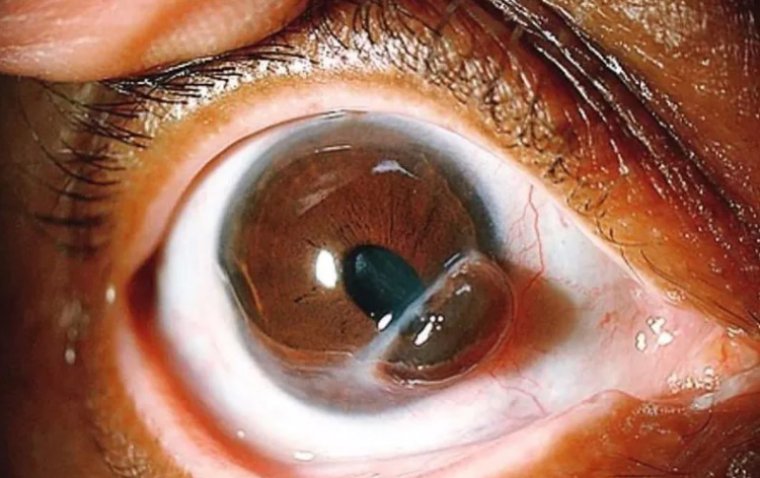
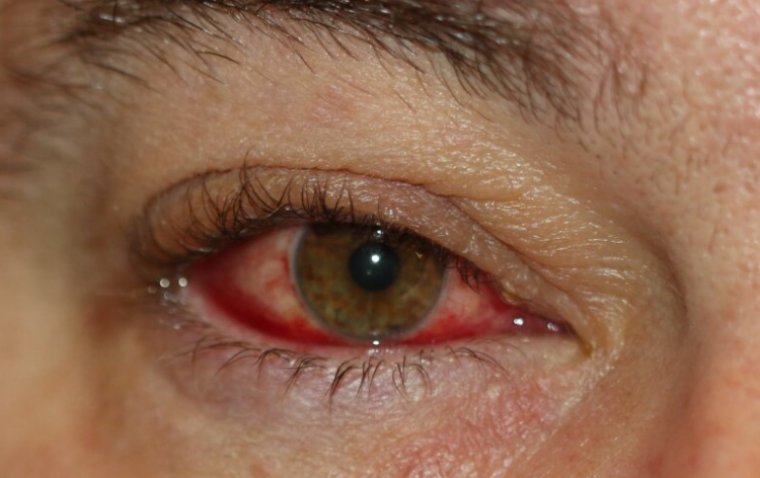
Blepharoconjunctivitis is a medical condition characterized by the simultaneous inflammation of the eyelids (blepharitis) and the conjunctiva, which is the membrane covering the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids. This condition often results in discomfort, redness, and irritation in the affected areas. The conjunctiva's proximity and interaction with the eyelids mean that inflammation in one can easily spread to the other, leading to this combined condition.
Types of Blepharoconjunctivitis
Blepharoconjunctivitis can be classified into two main types based on the area of the eyelids affected: Anterior and Posterior Blepharoconjunctivitis.
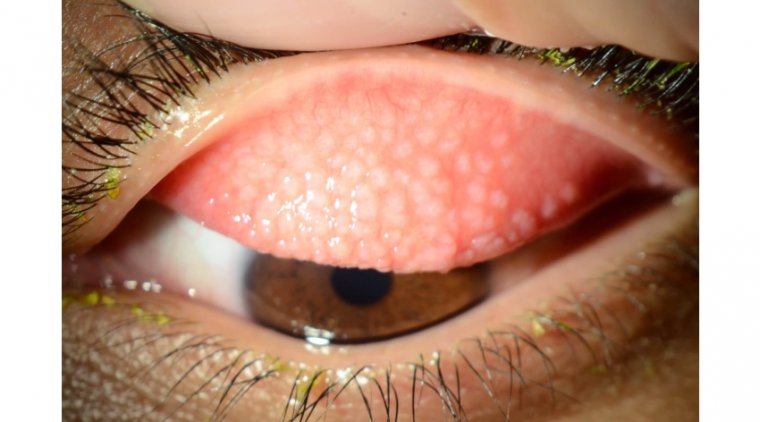
1. Anterior Blepharoconjunctivitis: This type affects the front part of the eyelids, particularly the area around the eyelashes and the outer skin of the eyelids. It is often associated with bacterial infections or seborrheic dermatitis. The symptoms typically include redness, swelling, and the presence of crusts or scales around the eyelashes. Itching and irritation are also common in this form.
2. Posterior Blepharoconjunctivitis: This form impacts the inner part of the eyelids, where the meibomian glands are located. These glands produce the oily part of the tear film, which is essential for eye lubrication. Posterior blepharoconjunctivitis is often linked to dysfunctions of these glands, leading to conditions like meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD). Symptoms include a gritty sensation in the eyes, tearing, and a feeling of dryness or burning. The inner eyelid may also appear inflamed and red.
What Causes Blepharoconjunctivitis?
The causes of blepharoconjunctivitis can be diverse, often involving a combination of environmental, biological, and lifestyle factors. Common causes include:
● Bacterial Infection: Certain bacteria can lead to infections in the eyelids and conjunctiva. Staphylococcus species are commonly implicated.
● Allergic Reactions: Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can trigger allergic blepharoconjunctivitis.
● Demodex Infestation: The presence of Demodex mites, tiny parasites that live on human skin, particularly around the eyelashes, can cause inflammation.
● Seborrheic Dermatitis: This skin condition, which causes dandruff, can also affect the eyelids and contribute to inflammation.
● Dry Eyes: Chronic dry eye syndrome can exacerbate or trigger inflammation in the conjunctiva and eyelids.
Signs and Symptoms of Blepharoconjunctivitis
Blepharoconjunctivitis presents a range of noticeable signs and symptoms, which are key indicators of this eye condition. These include:
Redness: One of the most common signs is the redness of the eyes and eyelids, indicating inflammation.
Itching: Itchy eyes are a frequent symptom, often causing discomfort and the urge to rub the eyes.
Swelling: The eyelids may become swollen and puffy due to the inflammation.
Crusts or Scales on Eyelids: The presence of crusts or scales, particularly around the base of eyelashes, is a notable sign.
Tearing: Excessive tearing or watery eyes can occur, which is the body's response to irritation.
Sensitivity to Light: Increased sensitivity to light, known as photophobia, may be experienced by some individuals.
Gritty Sensation: A feeling as if there is something in the eye, often described as a gritty or sandy sensation, is a common symptom.
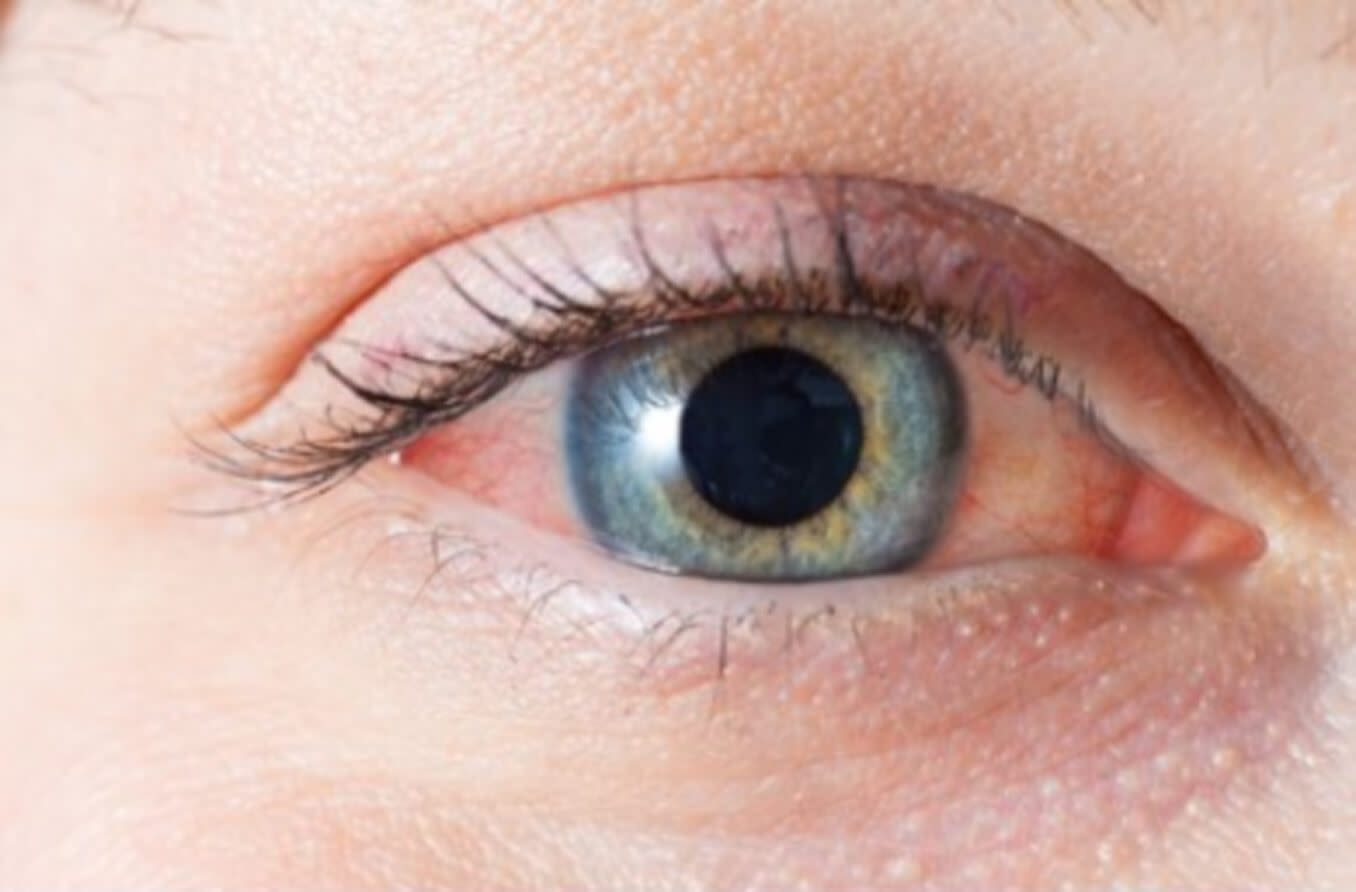
How is Blepharoconjunctivitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing blepharoconjunctivitis typically involves a comprehensive eye examination. Eye care professionals may perform the following:
● Visual Inspection: Examining the eyelids and conjunctiva for signs of inflammation.
● Slit Lamp Examination: Using a microscope to examine the eyes in detail.
● Swab Tests: To identify any bacterial or fungal infections.
● Allergy Testing: Particularly if an allergic cause is suspected.
Blepharoconjunctivitis Treatment
The treatment of blepharoconjunctivitis focuses on addressing the underlying cause and relieving symptoms:
1. Hygiene: Regular cleaning of the eyelids can help remove irritants and reduce inflammation.
2. Medicated Eye Drops: Depending on the cause, antibiotic, antifungal, or steroid eye drops may be prescribed.
3. Warm Compresses: These can help in loosening crusts and debris around the eyelids.
4. Artificial Tears: To alleviate dryness in cases related to dry eye syndrome.
5. Allergy Management: If allergies are a factor, antihistamine eye drops or oral medications may be recommended.
Is Blepharoconjunctivitis Contagious?
Blepharoconjunctivitis itself is not inherently contagious. This condition, characterized by the inflammation of both the eyelids and the conjunctiva, arises due to various factors that are not directly transmissible from person to person. However, it is crucial to understand that the underlying infections, particularly those caused by bacteria or viruses, which can lead to blepharoconjunctivitis, may indeed be contagious.
In cases where blepharoconjunctivitis is triggered by an infectious agent, such as certain bacteria or viruses, these organisms can spread from person to person. This transmission is typically through direct contact with infected secretions, often from the eyes or hands of an infected individual. Therefore, while the inflammatory condition itself is not contagious, the causative agents might be.
Importance of Hygiene
Given the potential for spreading infectious agents, adhering to proper hygiene practices is paramount in preventing the transmission of these infections. Some key hygiene practices include:
● Regular Hand Washing: Thoroughly washing hands with soap and water can significantly reduce the transmission of infectious agents.
● Proper Cleaning of Eyewear: Glasses, contact lenses, and other eyewear should be kept clean and handled with washed hands.
● Use of Personal Towels and Beddings: Sharing towels, pillows, and other personal items can be a route for spreading infections and should be avoided.
● Avoiding Close Contact: If suffering from an eye infection, it is advisable to limit close contact with others to reduce the risk of spreading the infection.
When to See an Ophthalmologist
It is important to know when to consult an ophthalmologist for blepharoconjunctivitis. You should seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, such as intense eye redness, swelling, pain, or changes in vision. These symptoms might indicate a more serious condition requiring professional intervention.
Additionally, if initial self-care measures or over-the-counter treatments do not alleviate symptoms within a reasonable timeframe, usually a few days, it's advisable to see an ophthalmologist. This is particularly important for individuals with pre-existing eye conditions, a weakened immune system, or those who wear contact lenses, as they may be more prone to complications. An ophthalmologist can provide a thorough examination, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment plan, which might include prescription medication or other specific interventions. Early consultation can prevent the progression of the condition and avoid potential long-term complications, ensuring the health and comfort of your eyes.
Summary
Blepharoconjunctivitis, characterized by the simultaneous inflammation of the eyelids and conjunctiva, is a condition that causes discomfort, redness, and irritation in the eye area. While not inherently contagious, it's important to note that the infectious agents causing it can be transmissible. Key causes include bacterial or viral infections, allergic reactions, Demodex infestation, seborrheic dermatitis, and dry eyes. Symptoms typically involve eye redness, swelling, itching, and sensitivity to light.
Diagnosis usually involves a comprehensive eye examination, which may include visual inspections, slit lamp examinations, and possibly swab tests or allergy testing. Treatment varies based on the underlying cause and may include hygiene practices, medicated eye drops, warm compresses, artificial tears, and allergy management.
Prevention focuses on maintaining good eyelid hygiene, avoiding allergens, and managing any underlying skin conditions. It's crucial to seek medical advice from an ophthalmologist if symptoms persist, worsen, or if initial treatments do not offer relief. Professional medical advice is essential for an accurate diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan, especially to prevent potential complications and ensure overall eye health.
(1).jpg)