Symblepharon: The Adhesion that Impacts Vision
What Is Symblepharon?
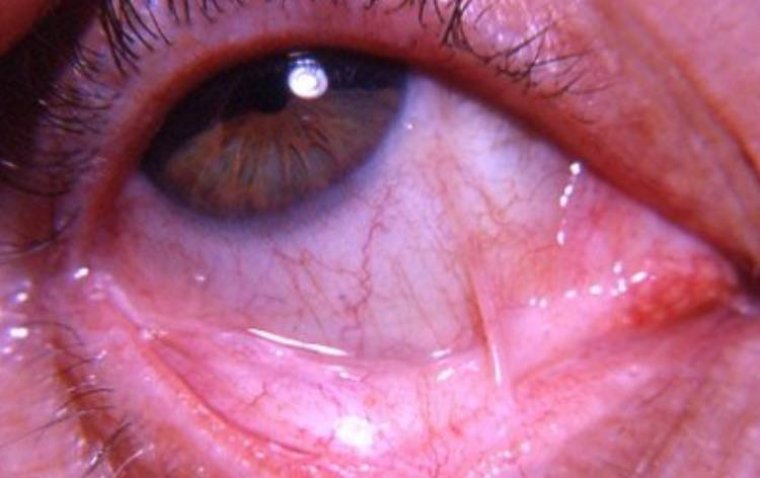
Symblepharon is a medical condition characterized by the adhesion of the conjunctiva, the clear membrane that covers the white part of the eye and the inside of the eyelids, to the cornea, the clear front part of the eye. This adhesion can cause pain, vision problems, and increased risk of infection.
What Causes Symblepharon?
Causes of symblepharon include inflammatory eye diseases such as vernal keratoconjunctivitis, trachoma, and autoimmune diseases such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Chemical or thermal burns to the eye, previous ocular surgeries such as corneal transplantation or glaucoma filtration surgery, and infections such as bacterial conjunctivitis can also lead to symblepharon.
Symptoms of Symblepharon
● Pain or discomfort in the affected eye
● Decreased vision or blurred vision
● Redness, swelling, and discharge in the affected eye
● Sensitivity to light
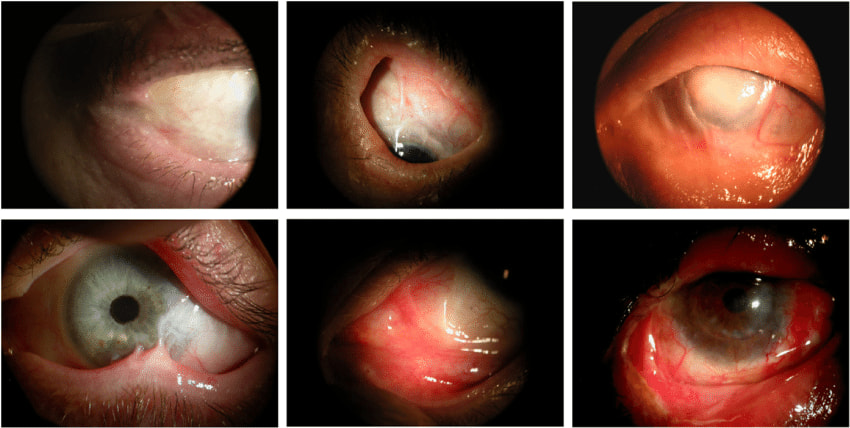
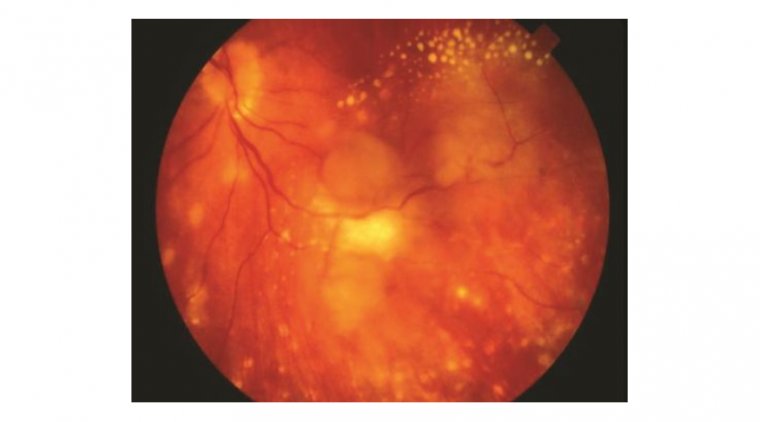
Photographs demonstrating symblepharon grading Credit: Research Gate
The symptoms of symblepharon may resolve on their own if the underlying cause of the adhesion is treated effectively. However, in some cases, the symptoms may persist even with treatment, particularly if the adhesion is extensive or has been present for a long time. The length of time it takes for the symptoms of symblepharon to pass varies depending on the severity of the condition, the underlying cause, and the type of treatment received.
Can Symblepharon Lead to Other Eye Problems?
Symblepharon can definitely lead to other eye problems. Because the conjunctiva is adhered to the cornea, the affected eye may be more susceptible to infections and inflammation, which can cause further damage to the eye and vision. In addition, symblepharon can cause the eyelid to turn inward, a condition known as entropion, which can lead to further discomfort and vision problems.
Symblepharon can also cause the cornea to become thin and scarred, which can affect vision and may lead to a condition known as corneal opacity. This can make it difficult for light to enter the eye and reach the retina, resulting in decreased vision.
In severe cases, symblepharon can also cause a loss of the tear film, which is essential for maintaining the health of the eye and vision. This can lead to dry eye syndrome, a condition in which the eye does not produce enough tears to keep the eye moist and comfortable.
Treatment Options for Symblepharon
Treatment options for symblepharon may vary based on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. The goal of treatment is to separate the conjunctiva from the cornea, restore the normal anatomy of the eye, and prevent further vision loss. Here are some common treatment options for symblepharon:
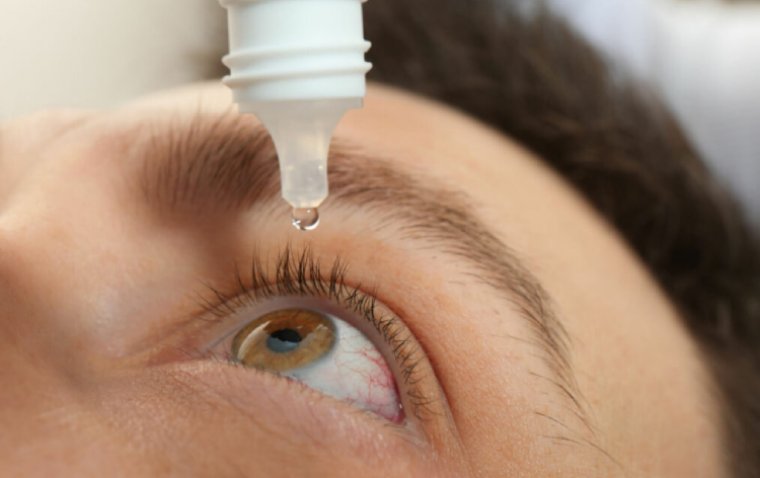
Corticosteroid eye drops: Corticosteroid eye drops can help reduce inflammation and prevent further scarring. They may be used to manage the symptoms of symblepharon, but are not a cure for the condition.
Antibiotic eye drops: Antibiotic eye drops may be prescribed to prevent or treat eye infections, which can be a common complication of symblepharon.
Artificial tears: Artificial tears can help to maintain the health of the eye and reduce the symptoms of dry eye syndrome. They can also help to prevent further scarring and vision loss.
Ointments: Ointments may be prescribed to provide additional moisture to the eye and help prevent further scarring.
Surgical intervention: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to separate the conjunctiva from the cornea and restore the normal anatomy of the eye. The procedure may involve a surgical separation of the conjunctiva from the cornea, or a procedure to correct the underlying cause of symblepharon, such as entropion.
In conclusion, symblepharon is a serious medical condition that can have a significant impact on a person's vision and quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of symblepharon, individuals affected by this condition can seek the support and care they need to manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
(1).jpg)