Macular Edema: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Imagine looking at your favorite painting or photograph and noticing that it's become blurry or distorted. You might try rubbing your eyes or adjusting the lighting, but the problem persists. This frustrating experience is similar to what people with macular edema may feel. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for macular edema to help you understand this condition and how it can be managed.
What Is Macular Edema?
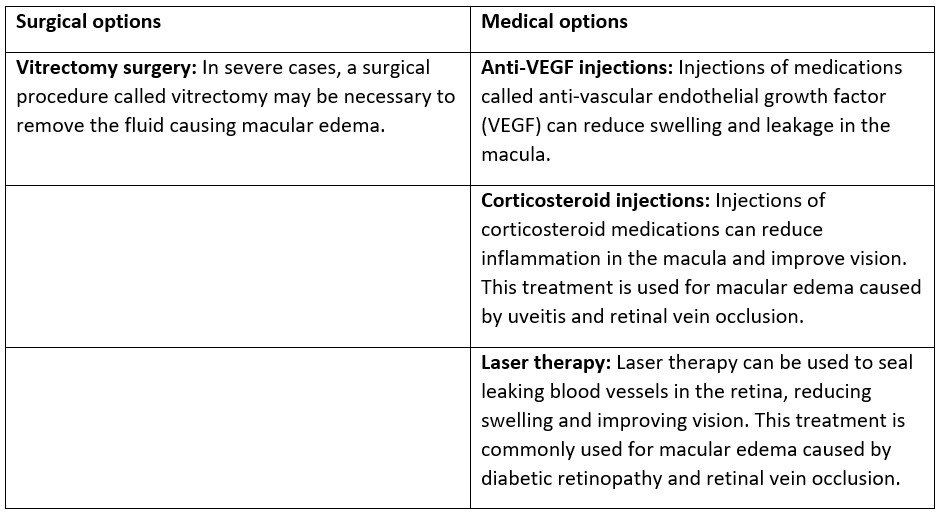
Macular edema is a condition in which fluid accumulates in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. This buildup of fluid can cause the macula to swell, resulting in distorted or blurred vision. Macular edema can occur as a complication of various eye diseases, including diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, uveitis, and retinal vein occlusion. It can also be caused by inflammation, eye injury, or side effects of certain medications. If left untreated, macular edema can lead to permanent vision loss. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of macular edema.
What Causes Macular Edema?
Macular edema can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
1. Diabetic retinopathy: This is the most common cause of macular edema. High blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, causing fluid to leak into the macula.
2. Age-related macular degeneration: This condition affects the macula and can cause fluid to accumulate in the area, leading to macular edema.
3. Uveitis: Inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye, can lead to macular edema.
4. Retinal vein occlusion: A blockage in the veins that carry blood away from the retina can cause fluid to leak into the macula.
5. Eye surgery or injury: Surgery or trauma to the eye can cause inflammation, which can lead to macular edema.
6. Inflammatory diseases: Certain diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, can cause inflammation that affects the macula.
7. Medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, can cause macular edema as a side effect.
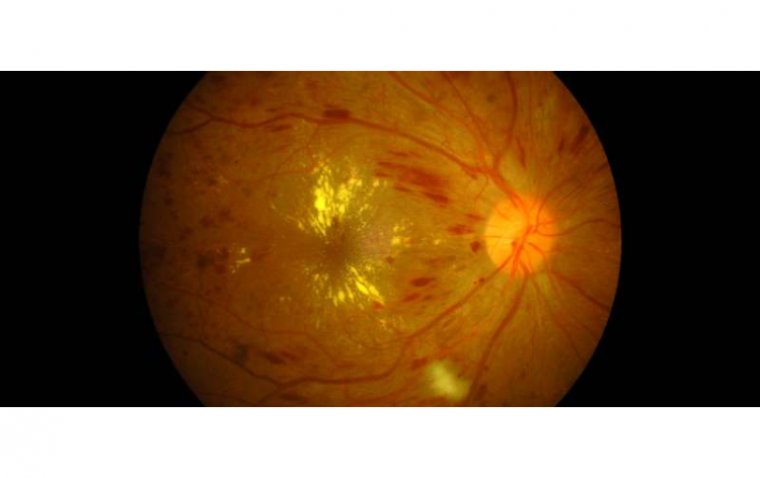
Macular Edema Credit: Retina Care Consultants
What Are the Symptoms of Macular Edema?
The symptoms of macular edema can vary depending on the severity of the swelling and the underlying cause of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
1. Blurred vision: Objects may appear blurry or hazy.
2. Distorted vision: Straight lines may appear wavy or crooked, and objects may appear stretched out or distorted.
3. Reduced central vision: A dark or blank spot may appear in the center of your vision, making it difficult to read, recognize faces, or perform other activities that require sharp central vision.
4. Decreased color perception: Colors may appear less vibrant or washed out.
5. Difficulty seeing in low light: People with macular edema may have difficulty seeing in low light conditions, such as at night or in dimly lit rooms.
6. Double vision: In rare cases, macular edema can cause double vision.
If you experience any changes in your vision, it is important to see an eye doctor for a comprehensive eye exam. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent vision loss.
Treatment Options for Macular Edema
What Is the Best Treatment for Macular Edema?
The best treatment for macular edema depends on the underlying cause of the condition, the severity of the swelling, and other individual factors. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary to achieve the best results. Some common treatments for macular edema include:
1. Anti-VEGF injections: Injections of medications called anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) can reduce swelling and leakage in the macula. This treatment is commonly used for macular edema caused by diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration.
2. Corticosteroid injections: Injections of corticosteroid medications can reduce inflammation in the macula and improve vision. This treatment is used for macular edema caused by uveitis and retinal vein occlusion.
3. Laser therapy: Laser therapy can be used to seal leaking blood vessels in the retina, reducing swelling and improving vision. This treatment is commonly used for macular edema caused by diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusion.
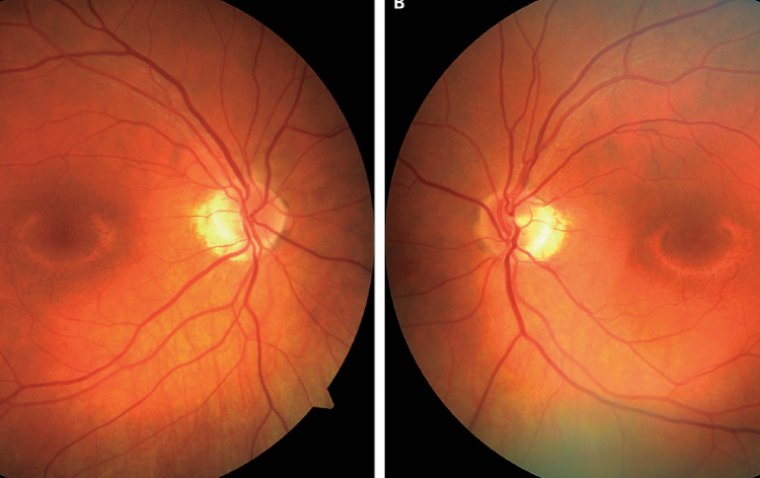
4. Vitrectomy surgery: In some cases, a surgical procedure called vitrectomy may be necessary to remove the fluid causing macular edema. This treatment is usually reserved for severe cases that have not responded to other treatments.
5. Lifestyle changes: Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and blood pressure can help prevent and manage macular edema caused by diabetes and hypertension. Avoiding smoking and getting regular eye exams can also help detect macular edema early and prevent vision loss.
Prevention of Macular Edema
Preventing macular edema involves managing the underlying conditions that can cause the swelling in the macula. Some ways to prevent macular edema include:
● Managing diabetes: Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing diabetic retinopathy, which is a common cause of macular edema.
● Controlling blood pressure: High blood pressure can damage blood vessels in the eye, leading to macular edema. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes or medications can help prevent the condition.
● Quitting smoking: Smoking is a risk factor for a number of eye conditions, including macular edema. Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
● Getting regular eye exams: Regular eye exams can help detect eye conditions like macular edema early on, when treatment is most effective.
It is important to note that some cases of macular edema may not be preventable, as they can be caused by factors like age-related macular degeneration or retinal vein occlusion. However, managing underlying conditions and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help reduce the risk of developing macular edema.
Author: Dr. Muhammad Saad, Resident Ophthalmologist at Al-Shifa Trust Eye Hospital in Rawalpindi, Pakistan
(1).jpg)