Dermolipoma: A Rare Benign Tumor of the Eye
Dermolipoma (Orbital Lipodermoid) is a rare, benign tumor that usually appears on the conjunctiva or the eyelid. It is composed of fatty and fibrous tissue and may develop in one or both eyes. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of dermolipoma, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What Causes Dermolipoma?
The exact cause of dermolipoma is still unknown. However, some researchers believe that it may be due to a congenital abnormality that occurs during embryonic development. Dermolipoma can also be associated with other eye conditions, such as strabismus (misaligned eyes) and ptosis (drooping eyelid). In rare cases, it may be associated with genetic disorders such as Goldenhar syndrome.
Symptoms of Dermolipoma
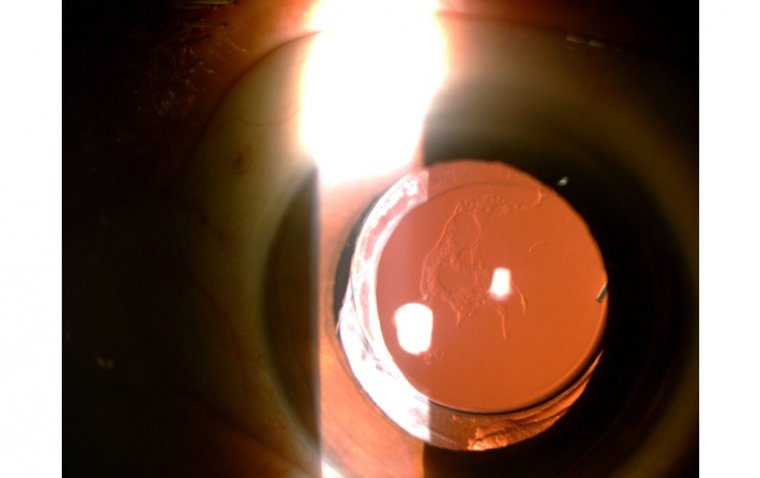
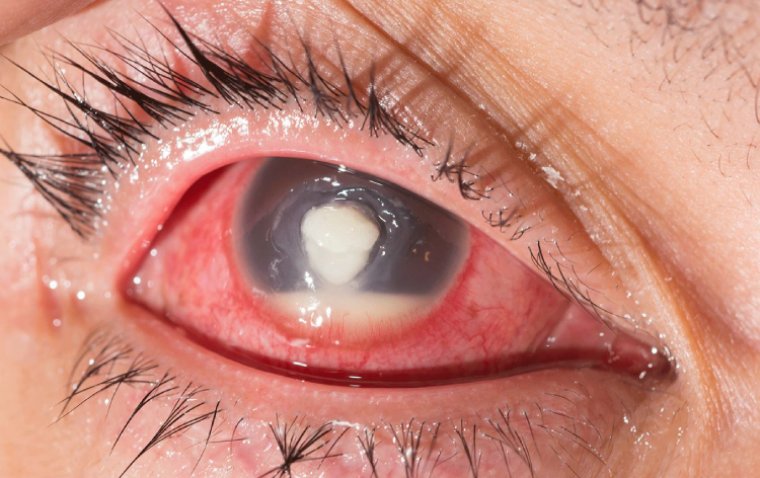
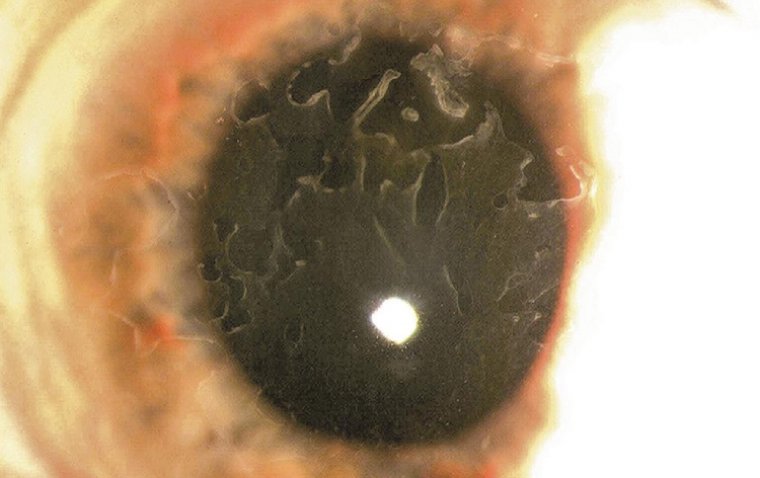
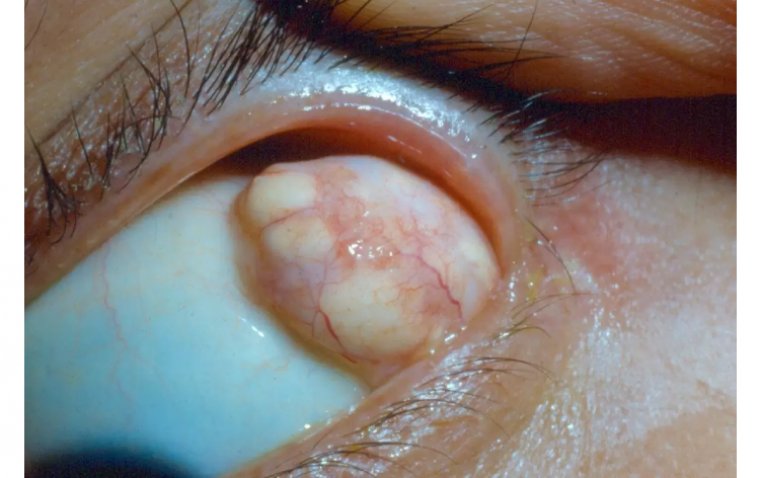
Dermolipoma is usually asymptomatic, which means it does not cause any discomfort or pain. It appears as a small, yellowish mass on the conjunctiva or eyelid. It may be visible only when the affected person looks up or down. In some cases, it may cause mild irritation, watering, or redness of the eye.
Dermolipoma Credit: EyeWiki
Diagnostic Procedures
There are various diagnostic tools that can be used to identify and diagnose dermolipoma, including:
1. Visual Examination: The first and most basic diagnostic tool is a visual examination of the affected area. The doctor will visually inspect the area around the eye and the eyelid to determine the presence and size of the dermolipoma.
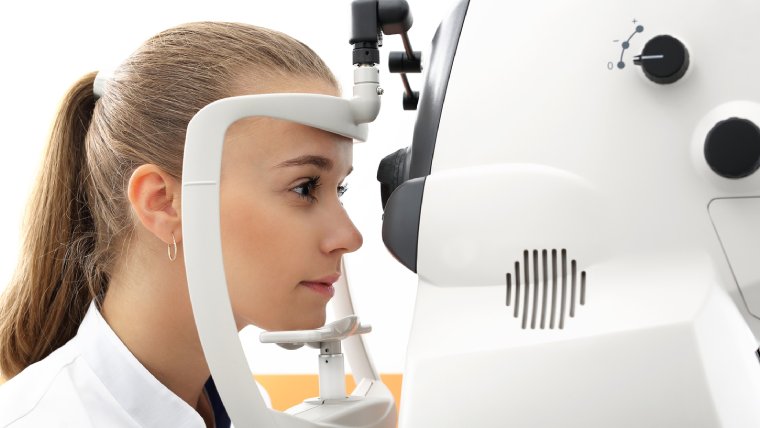
2. Slit Lamp Examination: A slit lamp examination is a more detailed examination of the eye that uses a special instrument called a slit lamp. The doctor can examine the eye under high magnification and light, which can help identify the presence and characteristics of the dermolipoma.
3. Biopsy: A biopsy involves removing a small piece of tissue from the dermolipoma and examining it under a microscope. This can help confirm the diagnosis and rule out any other potential conditions.
4. Imaging Studies: Imaging studies such as CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasound can be helpful in identifying the size and location of the dermolipoma, particularly if it is deep within the eye or surrounding structures.
5. Ophthalmoscopy: This is a non-invasive test that involves examining the inside of the eye with a special instrument called an ophthalmoscope. It can help identify any changes in the optic nerve or retina that may be caused by the dermolipoma.
6. Visual Field Testing: This is a test that measures the range of vision of the affected eye. It can help determine if the dermolipoma is affecting vision and to what extent.
7. Refraction Testing: This is a test that measures the degree of nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism. It can help determine if the dermolipoma is causing any changes in the refractive error of the eye.
Managing Dermolipoma
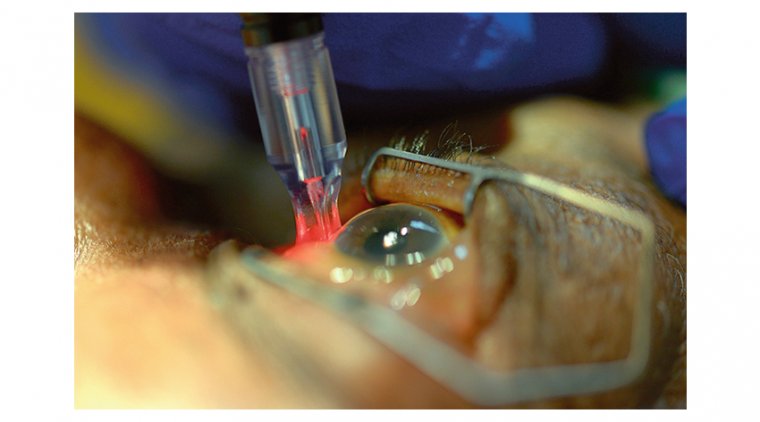
Dermolipoma is a benign tumor and does not require treatment unless it causes discomfort or affects vision. In cases where the tumor is causing irritation, watering, or redness, it may be surgically removed. The surgery is performed under local anesthesia and involves making a small incision to remove the tumor. In some cases, the tumor may recur, and the surgery may need to be repeated.
To conclude…
Dermolipoma is a rare, benign tumor that usually appears on the conjunctiva or eyelid. It is usually asymptomatic and does not require treatment unless it causes discomfort or affects vision. Surgical removal is the treatment of choice in cases where the tumor is causing irritation or redness. Although rare, regular eye exams can help detect and monitor the condition.
(1).jpg)