SMILE vs LASIK: Which Option is Right for You?
In the realm of refractive surgery, individuals seeking visual freedom are presented with a plethora of options. Two prominent procedures, SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction) and LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis), have emerged as front-runners, each with its unique benefits and considerations.
This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of these procedures, aiding prospective patients in making informed decisions based on their specific needs, preferences, ocular conditions, and targeted diseases.
What is SMILE?
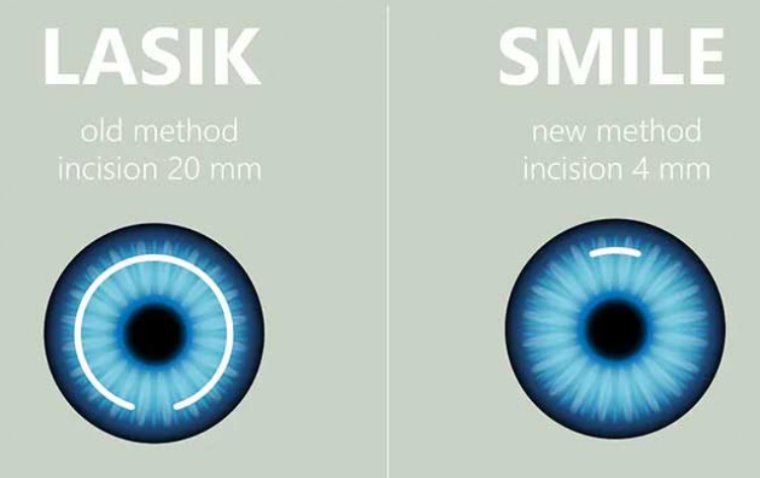
SMILE, which stands for Small Incision Lenticule Extraction, is a type of refractive eye surgery used to correct vision problems, primarily myopia (nearsightedness) and astigmatism. It is considered a minimally invasive alternative to traditional laser eye surgeries such as LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis). This minimally invasive procedure employs femtosecond laser technology.
What is LASIK?
LASIK, or Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis, is a widely performed refractive eye surgery that aims to correct common vision problems, such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism. LASIK is known for its effectiveness in reducing or eliminating the need for glasses or contact lenses. It is a widely embraced procedure that utilizes either a microkeratome or femtosecond laser to create a corneal flap.
Factors to Consider
1. Suitability:
● SMILE may be more suitable for individuals with thin corneas or dry eyes and is often recommended for myopia and astigmatism.
● LASIK is versatile, catering to various refractive errors, making it applicable for myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
2. Recovery Time:
● SMILE often boasts a quicker recovery, with less discomfort and faster visual stabilization, making it a suitable option for myopia and astigmatism.
● LASIK may entail a slightly longer recovery period, with some patients experiencing temporary dryness and discomfort, but it is effective for myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
3. Corneal Integrity:
● SMILE preserves a greater amount of corneal tissue, potentially contributing to enhanced corneal biomechanics, and is effective for myopia and astigmatism.
● LASIK involves creating a corneal flap, which may impact corneal stability, but is versatile and can address myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
Advantages and Disadvantages
1. SMILE:
Advantages:
● Minimally invasive with a small incision.
● Reduced risk of dry eyes.
● Potential for enhanced corneal biomechanics.
● Particularly effective for myopia and astigmatism.
Disadvantages:
● Limited availability compared to LASIK.
● Longer surgical learning curve for practitioners.
2. LASIK:
Advantages:
● Established and widely practiced.
● Versatile for various refractive errors.
● Rapid visual recovery for many patients.
● Effective for myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
Disadvantages:
● Corneal flap creation may lead to temporary dry eyes.
● Slightly longer recovery time for some individuals.
How to Decide Which Option is Better for You?
1. Consultation: Prioritize a comprehensive eye examination and consultation with an experienced refractive surgeon.
2. Personal Preferences: Consider factors such as recovery time, tolerance for discomfort, and individual lifestyle.
3. Eye Condition: Evaluate the severity and type of refractive error, corneal thickness, and overall eye health to inform the decision.
Conclusion
Both SMILE and LASIK stand as effective and safe refractive procedures, tailored to meet the diverse needs of patients with specific targeted diseases such as myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism. Deciding between the two requires a collaborative effort with a qualified eye care professional, who can provide personalized guidance based on individual preferences, ocular conditions, lifestyle considerations, and the specific diseases being addressed. In navigating this pivotal decision, the pursuit of visual clarity is matched only by the pursuit of a procedure that aligns seamlessly with one's unique circumstances.
(1).jpg)