Vision Therapy: What It Is and Who Can Benefit From It
Vision therapy is a specialized form of optometric care that utilizes a series of customized visual exercises and equipment to improve visual skills and processing. Often described as physical therapy for the eyes and brain, vision therapy aims to enhance the visual system's ability to perform more efficiently and comfortably. This article provides a comprehensive look at what vision therapy is, its benefits, who can benefit from it, and common questions surrounding the practice.
What is Vision Therapy?
Vision therapy is a clinical approach to correcting and improving visual deficiencies and disorders that are not adequately addressed by eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery alone. It involves a series of personalized activities and exercises prescribed by an optometrist to improve the coordination and functionality of the eye muscles, as well as the visual processing abilities of the brain.
Who Can Benefit from Vision Therapy?
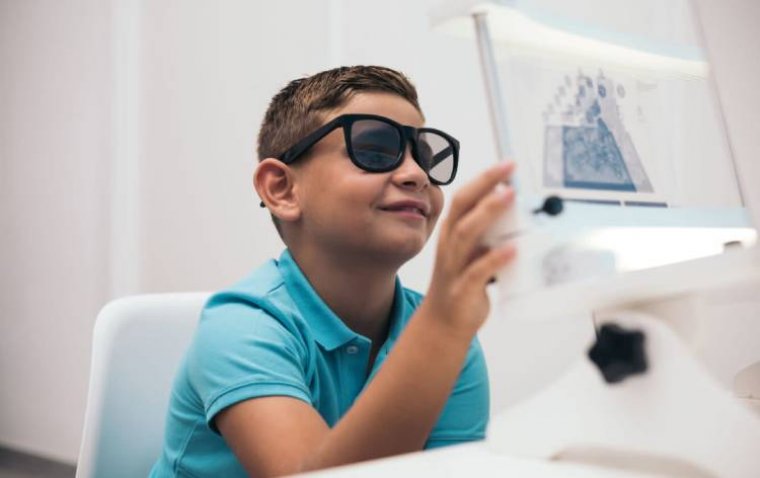
Children and Learning
(1).jpg)
Children who struggle with reading, writing, and staying focused in school may have underlying visual problems that go undetected in standard vision screenings. Common visual issues in children that can be treated with vision therapy include:
● Convergence insufficiency
● Amblyopia (lazy eye)
● Strabismus (crossed eyes)
● Eye movement disorders
Adults with Visual Stress
.jpg)
Vision therapy is not only for children; adults can also benefit. Those who suffer from visual stress due to extensive computer use or other activities that require sustained visual effort can experience relief through tailored therapy sessions. Symptoms such as headaches, blurred vision, and eye strain can often be alleviated with vision therapy.
Athletes Seeking Performance Enhancement
.jpg)
Athletes across a wide range of sports can benefit from vision therapy by improving their visual accuracy and reaction times. Customized programs can help enhance skills such as eye tracking, depth perception, and dynamic visual acuity.
The Goals of Vision Therapy
The goals of vision therapy are diverse and tailored to the individual needs of each patient. Generally, vision therapy aims to achieve several key objectives:
1. Improve Visual Efficiency: Vision therapy helps enhance the overall function of the visual system. This includes improving eye coordination, alignment, focusing abilities, and eye movement skills. The aim is to make visual tasks, like reading or using a computer, more comfortable and efficient.
2. Enhance Visual Processing: The therapy works on improving how visual information is processed by the brain. This not only involves the physical aspects of seeing but also the cognitive processes involved in interpreting what is seen.
3. Correct Visual Problems: Vision therapy can address specific visual problems such as strabismus (misalignment of the eyes), amblyopia (lazy eye), and binocular vision problems (issues with eye teaming). It helps train the eyes to work together effectively, which is crucial for good depth perception and 3D vision.
4. Support Developmental Improvements: Particularly in children, vision therapy can be crucial for developmental improvements related to vision, which can enhance learning, comprehension, and educational outcomes.
5. Reduce Visual Stress and Eye Strain: For both children and adults, vision therapy can help reduce symptoms of eye strain, headaches, and visual stress, particularly those symptoms that result from intensive screen use, reading, or other close-up tasks.
6. Prevent Vision and Learning Issues: In children, early intervention with vision therapy can prevent or mitigate learning difficulties that stem from vision issues, such as problems with reading, writing, and attention focus.
7. Enhance Sports Performance: Athletes might use vision therapy to improve their visual skills related to sports, such as dynamic visual acuity, eye tracking, and depth perception, which can enhance performance and reaction times.
Key Components of Vision Therapy
In-Office Sessions
Vision therapy typically involves weekly sessions with an optometrist, lasting about 30 to 60 minutes each. During these sessions, patients engage in controlled visual activities that are designed to correct their specific visual issues.
At-Home Exercises
In addition to in-office treatments, patients are often given exercises to perform at home to reinforce the skills learned during therapy sessions. These exercises are an integral part of the therapy’s success.
Specialized Equipment
A variety of tools and devices are used in vision therapy, including:
● Therapeutic lenses
● Prisms
● Filters
● Computer software
● Balance boards
Summary
Vision therapy offers a promising alternative or complement to traditional vision correction methods. By addressing the underlying issues of visual efficiency and processing, it can significantly improve the lives of individuals who struggle with a variety of visual challenges. Whether for academic success, workplace comfort, or sports performance, vision therapy can provide substantial benefits.
For those interested in exploring vision therapy, it is recommended to consult with a qualified optometrist who can provide a comprehensive eye exam and determine the most effective therapy plan for your specific needs.
(1).jpg)