Hyperopia (Farsightedness) - Understanding the Condition
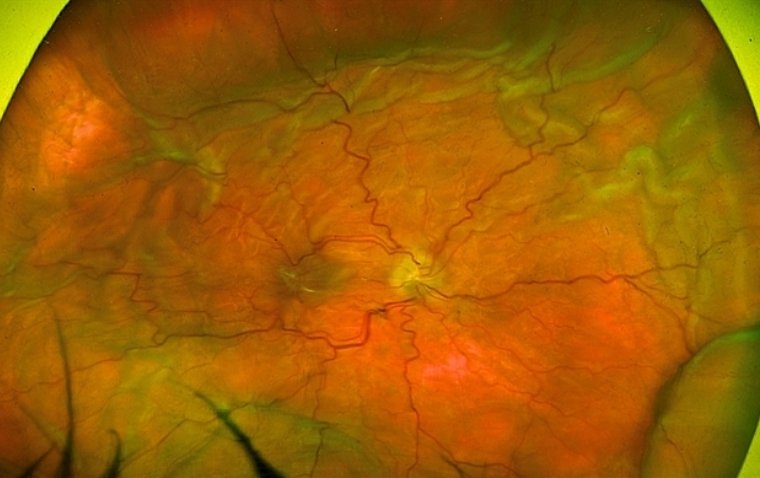
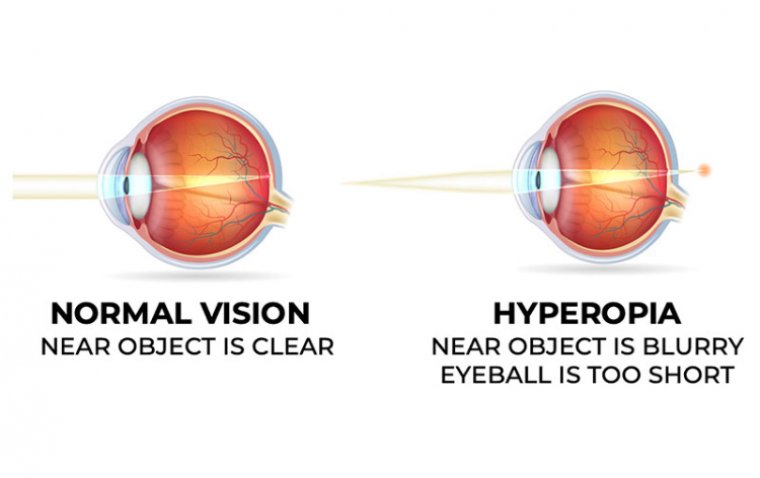
Hyperopia, also known as farsightedness and hypermetropia, is a refractive error of the eye that affects a person's ability to see objects at close range. In this condition, light entering the eye is focused behind the retina instead of on it, leading to blurred vision. Hyperopia is a common vision problem, affecting about 5-10% of the population. It can affect people of all ages, but it is more common in older adults.
What Causes Hyperopia?
Hyperopia occurs when the eyeball is shorter than normal, or the cornea has a less-than-ideal curvature. These factors cause light entering the eye to be focused behind the retina instead of on it, leading to blurred vision. Hyperopia may also be caused by the natural aging process, which can lead to a loss of elasticity in the lens of the eye. In some cases, hyperopia may be hereditary, meaning that it runs in families.
Symptoms of Hyperopia
The symptoms of hyperopia can vary from person to person, depending on the severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
● Blurred vision when looking at objects up close
● Difficulty reading or doing close work
● Eye strain or fatigue
● Headaches after doing close work
● Squinting or eye rubbing
● Difficulty seeing objects at a distance, especially at night
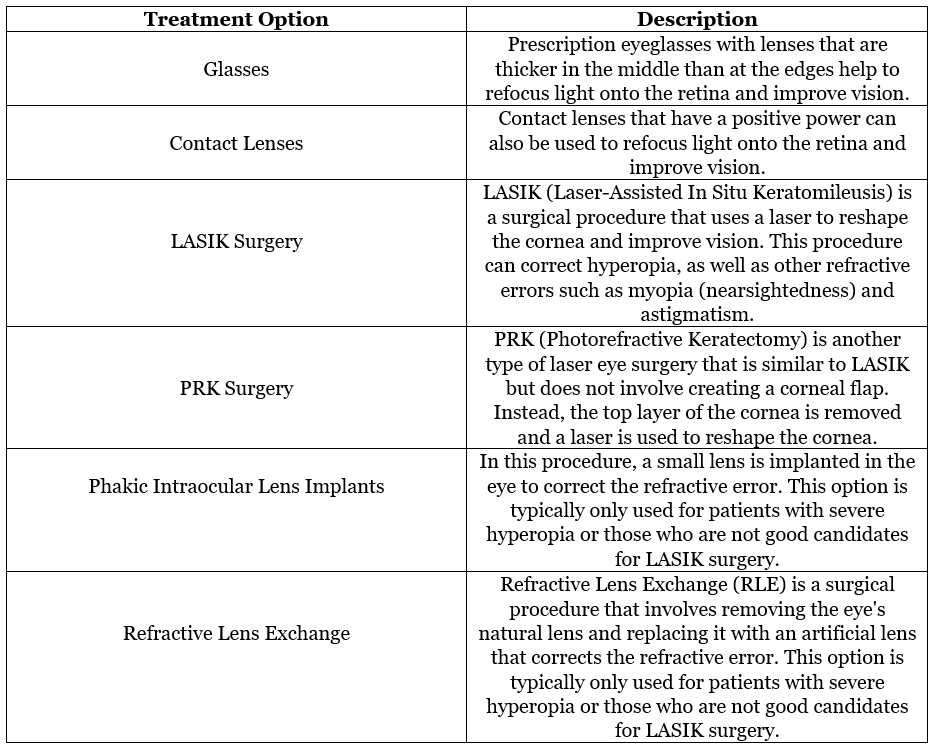
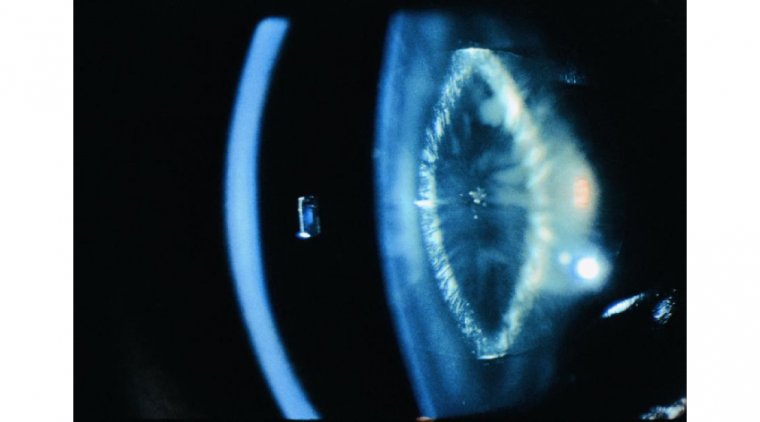
Treatment Options for Hyperopia
It's important to note that not all treatment options may be suitable for every individual, and the best course of action will depend on a variety of factors, such as the severity of the hyperopia and the patient's overall eye health. An eye doctor can help determine the most appropriate treatment option for each individual.
How to Prevent Hyperopia
While hyperopia is often hereditary and cannot be prevented, there are steps you can take to protect your eyes and maintain good eye health. Some tips include:
● Getting regular eye exams to detect and treat vision problems early
● Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which can help to protect against age-related eye problems
● Wearing protective eyewear when playing sports or doing activities that could cause eye injury
● Taking regular breaks when doing close work or using a computer, to reduce eye strain
● Avoiding smoking, which can increase the risk of age-related eye problems.
In conclusion, hyperopia is a common vision problem that affects many people. While it cannot always be prevented, early detection and treatment can help to maintain good eye health and prevent complications. If you experience any symptoms of hyperopia, it is important to see an eye doctor for an eye exam.
(1).jpg)