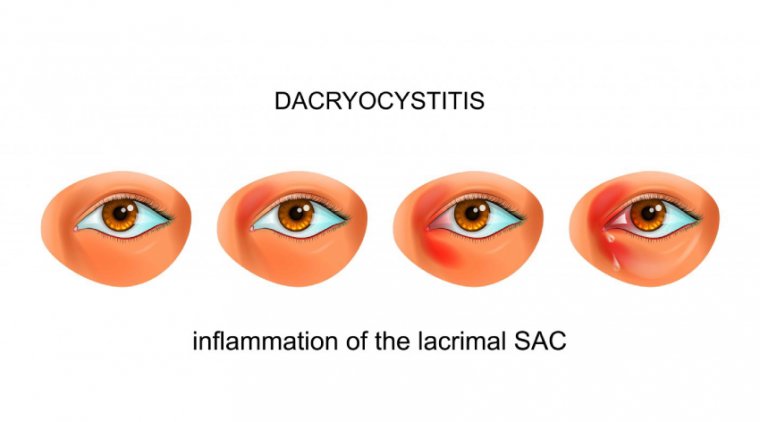
Dacryocystitis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Dacryocystitis is an infection or inflammation of the tear sac, which is located at the corner of the eye near the nose. The tear sac is responsible for collecting and draining tears from the eye to the nasal cavity. When this sac becomes blocked, bacteria can grow and cause an infection, leading to dacryocystitis. This condition can affect people of all ages, but it is more common in infants and the elderly.
Causes of Dacryocystitis
Here are some of the common causes of dacryocystitis:
Blocked tear ducts: The most common cause of dacryocystitis is a blocked tear duct, which can occur due to a congenital defect or an acquired condition like trauma or infection.
Bacterial infection: Dacryocystitis can be caused by a bacterial infection, which can occur due to poor eye hygiene or exposure to contaminated water or air.
Viral infection: Viral infections like herpes simplex virus, adenovirus, and varicella-zoster virus can cause dacryocystitis.
Fungal infection: Fungal infections like aspergillosis and candidiasis can cause dacryocystitis, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause inflammation of the tear drainage system, leading to dacryocystitis.
Tumors: Tumors in the nasal cavity or lacrimal sac can obstruct the tear drainage system and cause dacryocystitis.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy for cancer treatment can cause damage to the tear drainage system, leading to dacryocystitis.
Age-related changes: As people age, their tear drainage system may become narrower and less efficient, making them more susceptible to dacryocystitis.
Symptoms of Dacryocystitis
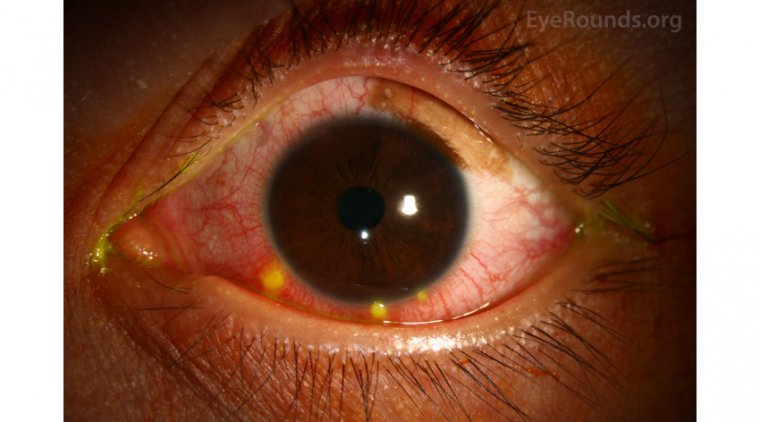
The symptoms of dacryocystitis can vary from person to person, but some common signs include redness, swelling, and tenderness in the corner of the eye near the nose. There may also be discharge, which can be clear or yellow and may have an odor. Other symptoms include tearing, blurred vision, and fever.
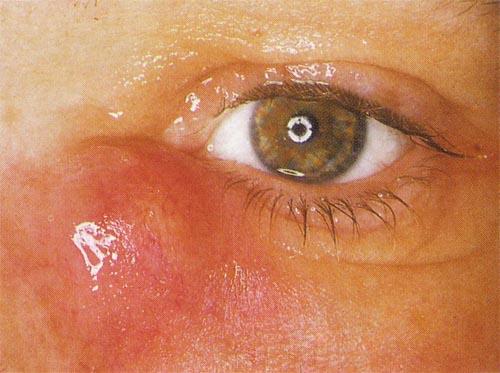
Treatment of Dacryocystitis
The treatment for dacryocystitis typically involves antibiotics to clear up the infection. Treatment options for dacryocystitis include:
● Warm compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected eye can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
● Antibiotics: Oral or topical antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial infections that cause dacryocystitis. The choice of antibiotic will depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection.
● Nasolacrimal duct probing and irrigation: This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible probe into the tear duct to open the blockage and flush out any debris or infection.
● Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) surgery: This procedure is performed to create a new drainage pathway for tears by bypassing the blocked tear duct. A small incision is made near the nose and a new passage is created between the tear sac and the nasal cavity.
● Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (endoDCR): This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses an endoscope to visualize and access the tear duct. It involves creating a new drainage pathway in a similar way as DCR, but through a smaller incision.
The choice of treatment will depend on the severity of the condition, the cause of the blockage, and the patient's overall health. It's important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have dacryocystitis as untreated infections can lead to serious complications such as orbital cellulitis.
Recovery Time and Complications of Dacryocystitis
With proper treatment, most people recover from dacryocystitis within a few weeks. However, if left untreated, the infection can spread and cause serious complications like cellulitis or orbital abscess. In rare cases, it can also lead to vision loss.
Recurrence of Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis can recur after treatment, especially if the underlying cause of the blockage is not addressed. It is important to follow your doctor's recommendations for preventing a recurrence, which may include regular eye exams and treatment for any underlying conditions.
To conclude...
Dacryocystitis is a relatively common condition that can cause discomfort and potentially serious complications. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications and promoting a speedy recovery. With proper care, most people can recover from dacryocystitis without any long-term effects.
(1).jpg)