Dacryoadenitis: Understanding Lacrimal Gland Inflammation
What Is Dacryoadenitis?
Dacryoadenitis is an inflammatory condition that specifically targets the lacrimal glands, the glands responsible for tear production. Located in the upper outer region of each eye, these glands play an essential role in maintaining eye health by producing tears to lubricate the eye surface. Tears also contain enzymes that help to combat bacterial infections.
Inflammation of the lacrimal gland can result in inadequate tear production, leading to dry eyes, discomfort, and a higher risk of eye infections. Dacryoadenitis, therefore, can have a significant impact on both comfort and the overall health of the eyes.
Dacryoadenitis vs Dacryocystitis
Both dacryoadenitis and dacryocystitis are inflammatory conditions that affect the eye, but they target different structures and have distinct symptoms and causes.
Dacryoadenitis:
● Target Area: Inflammation occurs in the lacrimal gland, which is responsible for tear production.
● Symptoms: Swelling and tenderness in the upper, outer corner of the eye; reduced tear production that may lead to dry eyes; redness; fever; and occasionally, systemic symptoms if the inflammation is part of a broader infection.
● Causes: Often caused by viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, or less commonly, tumors.
Dacryocystitis:
● Target Area: Inflammation occurs in the lacrimal sac, a structure that drains tears from the eye into the nose.
● Symptoms: Swelling and redness near the inner corner of the eye; pain; excessive tearing; pus discharge; and potentially fever.
● Causes: Usually caused by bacterial infections due to obstruction of the tear drainage system, and more rarely, by fungal infections or trauma.
What Causes Dacryoadenitis?
Dacryoadenitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the lacrimal gland, a crucial structure responsible for tear production. The causes can be broadly categorized into infectious and non-infectious origins:
Infectious Causes:
1. Bacterial Infections: Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species are common bacteria that can lead to dacryoadenitis. These bacterial infections often require antibiotic therapy for treatment.
2. Viral Infections: Viruses such as the mumps virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and herpes simplex can infect the lacrimal gland, leading to inflammation and symptoms like swelling and redness.
3. Fungal Infections: Though rare, fungi like Candida and Aspergillus can also affect the lacrimal gland and cause dacryoadenitis.
Non-Infectious Causes:
1. Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus can trigger inflammation in the lacrimal glands as part of a generalized autoimmune response.
2. Systemic Diseases: Conditions such as sarcoidosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis can lead to dacryoadenitis as they affect multiple organ systems, including the eyes.
3. Tumors: Though less common, benign or malignant tumors of the lacrimal gland can mimic the symptoms of dacryoadenitis and cause inflammation.
4. Idiopathic: In some cases, the cause of dacryoadenitis remains unknown despite thorough evaluation.
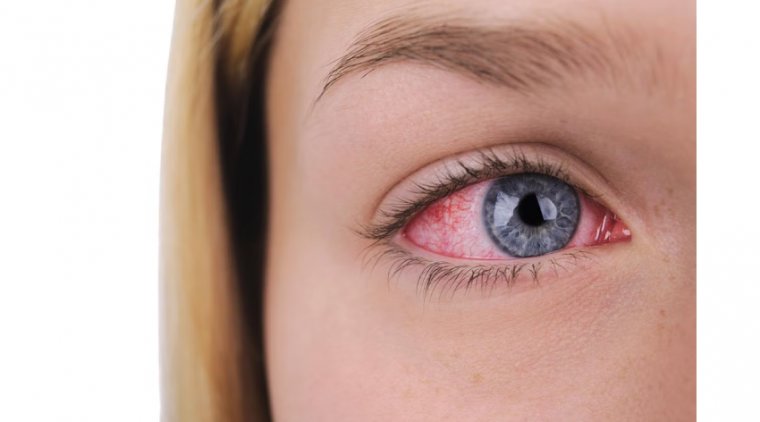
Dacryoadenitis Symptoms
The symptoms of dacryoadenitis can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. However, there are common symptoms that usually present in most cases:
Common Symptoms:
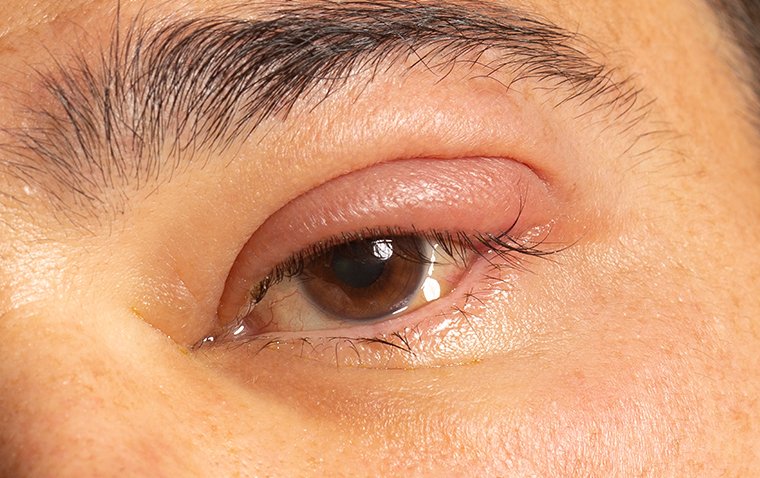
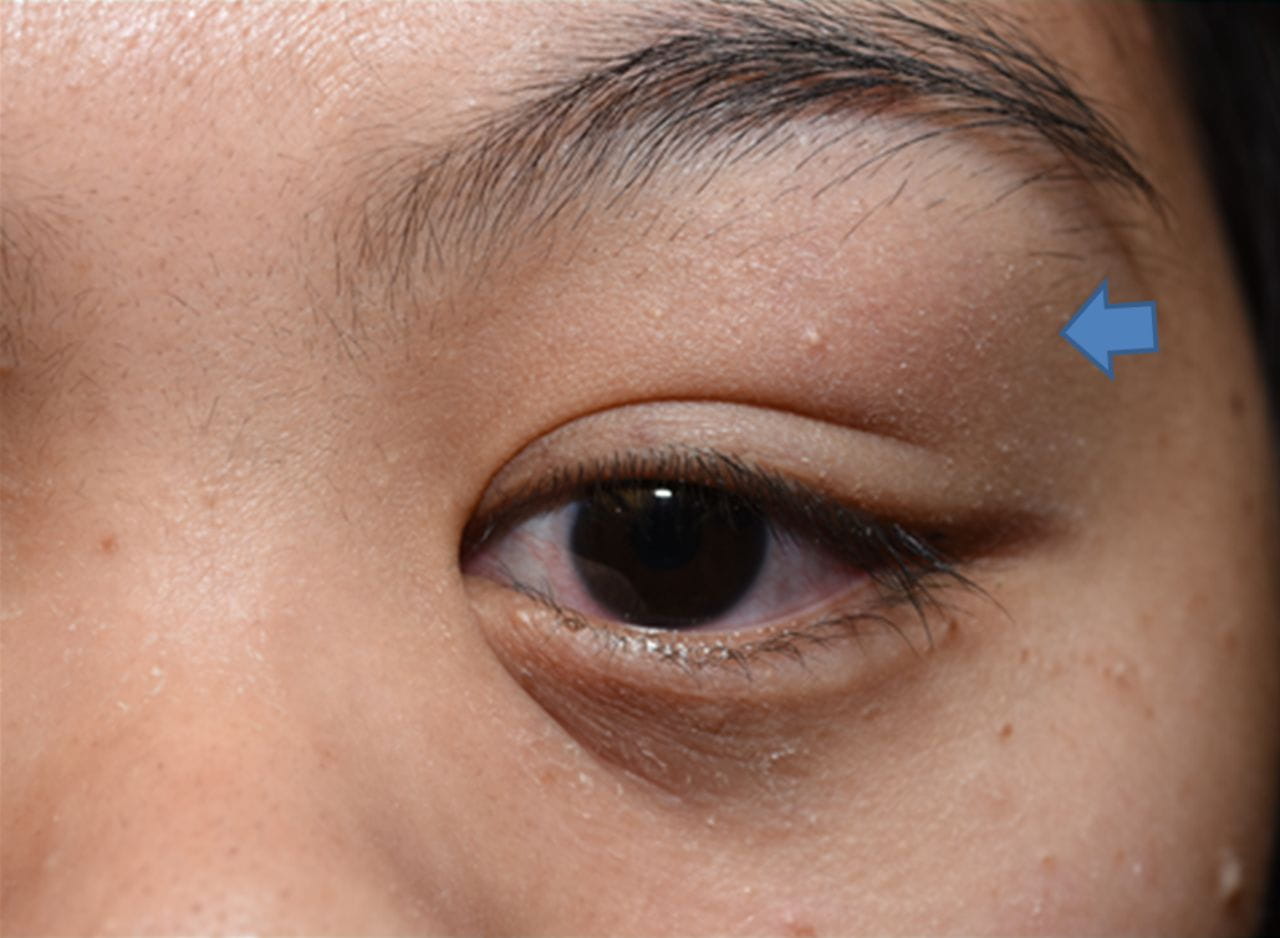
- Eye Pain: One of the most common complaints is a localized pain near the affected lacrimal gland, which is often aggravated by touch or eye movement.
- Swelling: Inflammation of the lacrimal gland often leads to noticeable swelling in the upper outer region of the eyelid.
- Redness: The affected area often becomes red and may have a warm feeling to the touch, indicating inflammation.
- Excessive Tearing: The lacrimal gland is responsible for tear production; therefore, its inflammation can result in an abnormal amount of tear secretion.
- Vision Disturbances: In severe cases, the swelling may cause vision issues, though this is less common.
Credit: BMJ
How to Diagnose Dacryoadenitis
Diagnosing dacryoadenitis accurately is crucial for the effective management of the condition. Given that its symptoms can be similar to other ocular or systemic conditions, a thorough diagnostic approach is essential. Here's how it is generally done:
1. Clinical Examination: The first step in diagnosis is a detailed clinical examination by an ophthalmologist. This involves a thorough history-taking to understand symptom onset, duration, and any related systemic issues. Physical examination of the eye and surrounding areas checks for the classic signs such as redness, swelling, and tenderness.
2. Imaging Studies
● Ultrasound: It is often used to evaluate the lacrimal gland and surrounding tissues. This non-invasive method can reveal the extent of swelling and any other abnormalities.
● MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI may be recommended for more detailed imagery, particularly if there are suspicions of a more severe or complicated underlying condition.
3. Biopsy: In cases where the cause of dacryoadenitis is unclear or if there is suspicion of a malignant condition, a biopsy of the lacrimal gland may be performed. This involves taking a small tissue sample for histological examination.
Differentiation from Similar Conditions:
Accurate diagnosis involves differentiating dacryoadenitis from other conditions that present with similar symptoms. These may include:
● Dacryocystitis: This condition involves inflammation of the lacrimal sac, rather than the gland, and often has different symptoms and causes.
● Cellulitis: This skin infection can mimic the symptoms of dacryoadenitis but generally lacks the specific involvement of the lacrimal gland.
● Chalazion or Stye: These eyelid issues can also cause localized swelling but are usually differentiated by the absence of more severe symptoms like eye pain or vision disturbances.
Dacryoadenitis Treatment
The treatment of dacryoadenitis is primarily guided by the underlying cause of the inflammation. Because this condition can result from a variety of causes, from bacterial infections to autoimmune diseases, a tailored treatment approach is often necessary. Here are some common treatment options based on causative factors:
Antibiotics for Bacterial Infections
● Oral Antibiotics: If bacterial infection is confirmed as the cause, a course of oral antibiotics such as amoxicillin-clavulanate or doxycycline may be prescribed.
● Topical Antibiotics: In some cases, topical antibiotic ointments or eye drops may also be used alongside oral medications for more effective treatment.
Anti-inflammatory Medications for Autoimmune-related Dacryoadenitis
● Corticosteroids: If dacryoadenitis is caused by autoimmune disorders or non-infectious inflammation, corticosteroid eye drops or systemic corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation.
● Immunosuppressive Agents: In severe cases, or those resistant to steroids, medications that modulate the immune system may be considered.
Supportive Measures
● Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected eye can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
● Artificial Tears: Over-the-counter lubricating eye drops can help manage symptoms like dryness and irritation.
● Pain Relief: Non-prescription pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used to manage pain, but should be used under medical advice.
How to Prevent Dacryoadenitis
Preventing dacryoadenitis largely involves general eye care and attentiveness to one's overall health. Here are some measures that can help minimize the risk of developing this condition:
Good Hygiene
● Handwashing: Regular and thorough handwashing with soap and water can prevent the spread of infectious agents that might cause dacryoadenitis.
● Avoid Eye Rubbing: Refrain from touching or rubbing your eyes, especially with unwashed hands, to reduce the risk of transferring bacteria or viruses to the eye area.
Avoid Eye Trauma
● Eye Protection: Use protective eyewear when engaging in activities that could lead to eye injury, such as sports or certain types of work.
● Caution with Chemicals: Always read and follow instructions when using household cleaning agents or chemicals, as accidental splashes can cause eye irritation and potentially lead to dacryoadenitis.
Managing Underlying Health Conditions
● Regular Check-ups: If you have an autoimmune condition or a systemic disease that could make you more susceptible to dacryoadenitis, regular medical check-ups are crucial for monitoring your eye health.
● Immunizations: Stay up-to-date on vaccinations, especially those that protect against viral or bacterial infections that could lead to dacryoadenitis, such as the flu vaccine.
Health Awareness
● Know the Signs: Early recognition of symptoms can lead to prompt treatment, reducing the risk of complications.
● Consult Your Doctor: If you are experiencing symptoms or have concerns about your risk factors, consult with a healthcare provider for tailored advice.
Summary
Dacryoadenitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the lacrimal gland, which plays an essential role in tear production and overall eye health. Distinguishing it from similar conditions like dacryocystitis is crucial for effective treatment. The condition can arise from a variety of causes, ranging from bacterial, viral, or fungal infections to non-infectious triggers like autoimmune disorders.
Symptoms commonly include eye pain, swelling, redness, and excessive tearing, though the presentation can vary based on the severity and underlying cause. Diagnosis involves a clinical examination complemented by imaging studies or biopsy, as needed. Treatment is tailored to the specific cause and may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, anti-inflammatory medications for autoimmune conditions, and supportive measures like warm compresses and artificial tears.
Prevention focuses on general eye care, including maintaining good hygiene, protecting the eyes from trauma, and managing underlying health conditions that may predispose you to dacryoadenitis.
(1).jpg)