The Biggest Challenges in Ophthalmology Today: Survey Insights
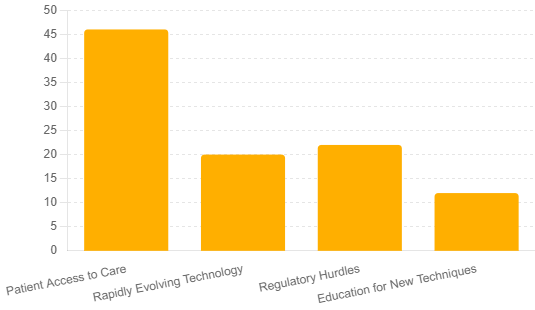
A recent survey conducted by OBN on LinkedIn asked participants to identify the most pressing challenge facing the ophthalmology field today. The poll revealed that nearly half of the respondents believe patient access to care is the primary issue, followed by regulatory hurdles, rapidly evolving technology, and education for new techniques.
Patient Access to Care: The Primary Challenge
Survey Result: 46% identified this as the top challenge.
Patient access to care is a cornerstone issue in ophthalmology, reflecting significant disparities that are deeply rooted in various socio-economic and geographical factors. The availability of ophthalmological services is unevenly distributed, with rural areas often facing critical shortages of specialists. This lack of access leads to delayed diagnoses and treatments, which can exacerbate conditions and contribute to preventable vision loss.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 2.2 billion people globally suffer from vision impairment, with nearly half of these cases being either preventable or untreated, highlighting the urgent need for more accessible care.
In the United States, the situation is further complicated by insurance coverage issues and the high costs associated with specialized eye care. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO), millions of Americans lack adequate vision care, increasing the risk of preventable blindness and vision impairment. Addressing these issues requires comprehensive changes, including the expansion of telemedicine, increased funding for public health initiatives, and policy reforms aimed at making eye care more affordable and accessible to all populations.
The number of ophthalmology practices has been declining, which could impact patient access. Between 2015 and 2022, the number of ophthalmology practices in the U.S. decreased by 18%, from 7,149 to 5,890. This consolidation means fewer individual practices are available, potentially limiting access, especially in rural areas.

A line chart showing the decline in the number of ophthalmology practices from 2015 to 2022 in U.S.
Wait times for certain ophthalmic procedures like cataract surgeries have shown signs of recovery post-pandemic. In 2023, 70% of cataract surgery patients in Canada were treated within the recommended 112 days, a significant improvement from 2020 when the figure dropped to 45%.
.jpg)
A bar graph showing the percentage of cataract surgery patients treated within 112 days from 2019 to 2023 in Canada.
Regulatory Hurdles: A Barrier to Innovation
Survey Result: 22% saw this as a significant challenge.
Regulatory challenges represent another significant obstacle in the field of ophthalmology, particularly concerning the approval and deployment of new treatments and technologies.
The stringent requirements set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and other global regulatory bodies, while essential for patient safety, often result in lengthy approval processes that can delay the availability of innovative therapies. These delays can be especially burdensome for smaller companies, which may lack the resources to navigate the complex regulatory landscape.
For instance, the approval process for new ophthalmic drugs and devices can take years, often leading to significant delays in bringing potentially life-changing treatments to patients. This not only affects the patients who are waiting for advanced therapies but also stifles innovation in the field. Streamlining these regulatory processes, while maintaining high safety standards, could help accelerate the introduction of new treatments, ensuring that patients benefit from the latest advancements in ophthalmology.
Rapidly Evolving Technology: Keeping Pace with Progress
Survey Result: 20% of respondents cited this as a challenge.
The pace of technological advancement in ophthalmology is both a blessing and a challenge. On one hand, new diagnostic tools, surgical techniques, and treatment options are continually improving patient outcomes.
On the other hand, the rapid evolution of technology presents significant challenges for clinicians, who must constantly stay updated with the latest developments. Integrating these new technologies into everyday practice can be particularly daunting for smaller clinics or those in resource-limited settings.
Take, for example, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) in ophthalmology. AI is increasingly being used to enhance diagnostic accuracy for conditions such as diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). However, the implementation of AI and other cutting-edge technologies requires substantial investment in both hardware and training.
This creates a barrier for some practitioners, particularly those in smaller or rural practices, who may struggle to afford or effectively integrate these advancements into their workflows. Ensuring that all ophthalmologists have the resources and training necessary to utilize these technologies is crucial for maximizing their potential benefits to patients.
Education for New Techniques: The Need for Continuous Learning
Survey Result: 12% identified education as a key challenge.
The need for continuous education is paramount in ophthalmology, especially given the field's rapid advancements in medical techniques and technologies. Staying current with new procedures and treatment modalities can be challenging for practitioners, particularly those who manage busy practices or work in regions with limited access to advanced training programs. Ongoing professional development is essential to ensure that ophthalmologists can provide the highest standard of care to their patients.
Programs like the AAO's Ophthalmic Education initiative offer valuable resources for continuing education, yet disparities in access to these opportunities persist. The fast pace of innovation means that traditional educational models may need to evolve, offering more flexible and accessible training options that cater to the needs of a diverse range of practitioners. By prioritizing education and professional development, the ophthalmology community can better equip its members to adopt and implement new techniques, ultimately improving patient care across the board.
Conclusion
The OBN survey provides critical insights into the multifaceted challenges facing the field of ophthalmology today. With patient access to care emerging as the most significant concern, it is clear that addressing this issue requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders in the ophthalmology community. However, regulatory hurdles, rapidly evolving technology, and the need for continuous education also present substantial challenges that must be tackled to ensure the continued advancement of the field.
(1).jpg)