Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
What Is Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
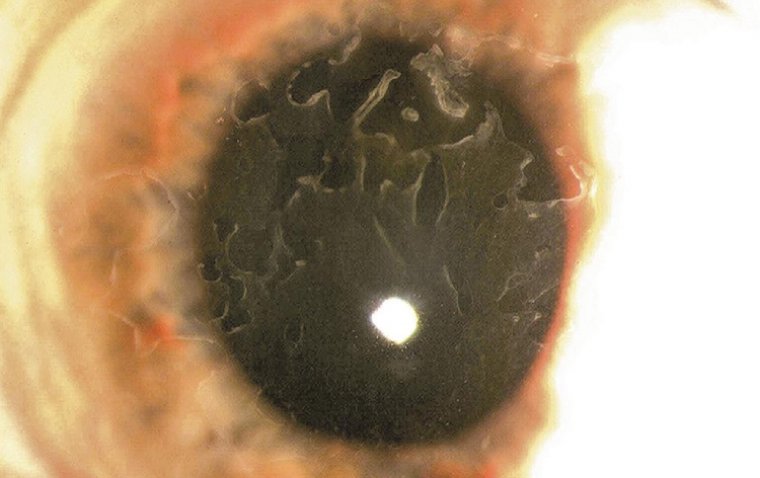
Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy (ABMD) is a prevalent corneal dystrophy that often goes unrecognized until it starts affecting our precious gift of sight. As the most common type of corneal dystrophy, ABMD affects the delicate front surface of the eye, known as the cornea, specifically its epithelial basement membrane. As a vital part of the eye, any disruption to this layer can have profound effects on our vision and overall quality of life.
Understanding ABMD, its causes, symptoms, and how it can be managed, is essential for those diagnosed with this eye disorder. It's through such knowledge that we can work towards not only managing the condition effectively but also preventing any potential complications that might arise. With our focus on Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy, or ABMD, we hope to shed light on this condition to ensure that anyone dealing with this type of corneal dystrophy has the necessary information to navigate their treatment journey.
What Causes Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy?
Unraveling the causes of Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy (ABMD) can give us a better understanding of the disorder, thus aiding in its effective diagnosis and management. While the exact origin of ABMD is not definitively known, research suggests it has a strong genetic link. In many cases, the condition is passed down through families, pointing to a hereditary pattern.
The disorder typically emerges due to abnormal proteins produced in the cornea, causing disruptions to the epithelial basement membrane. The mutations leading to these abnormal proteins are often inherited, following an autosomal dominant pattern. This means a child only needs to inherit a faulty gene from one parent to potentially develop the condition.
While genetic predisposition plays a significant role, it is also worth noting the possible influence of environmental factors. Some studies suggest that eye injury or other forms of trauma may trigger the onset of ABMD in individuals with a genetic susceptibility. However, more research is required to fully understand these contributing factors.
Symptoms of Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy
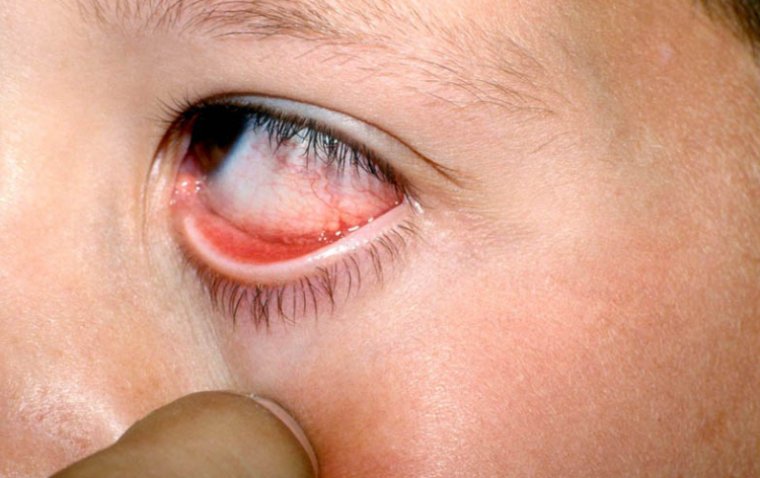
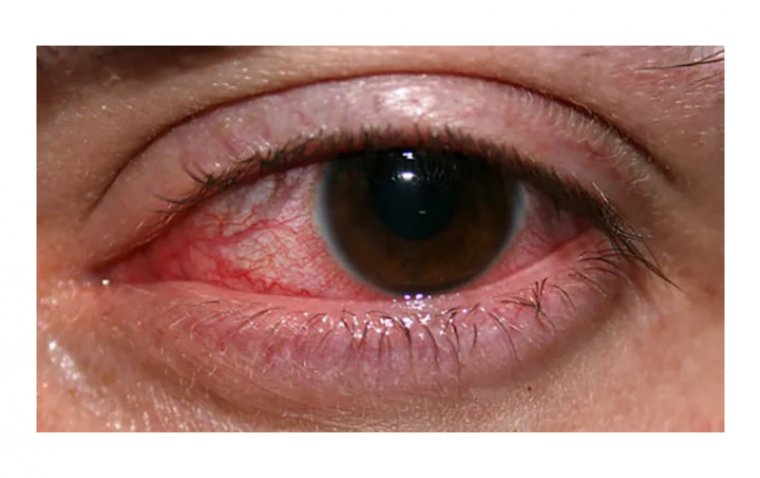
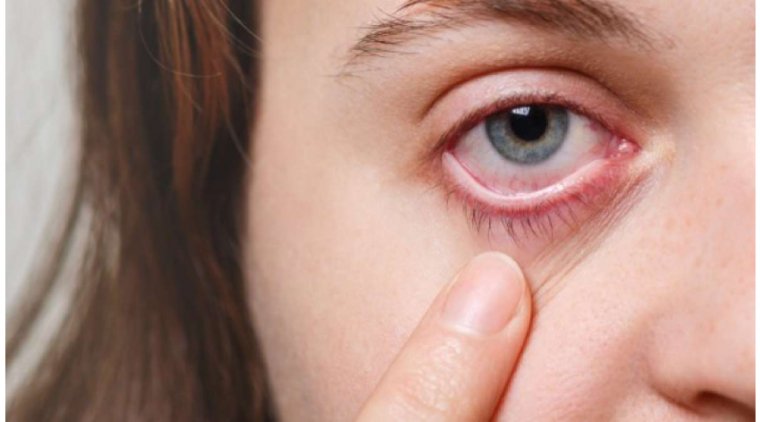
Individuals with Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy (ABMD) often present a range of symptoms that might initially be subtle, growing more noticeable over time. Common symptoms of this corneal dystrophy include blurred vision and a gritty or sandy feeling in the eyes, often described as foreign body sensation.
One of the more distinctive symptoms is recurrent corneal erosion. These erosions occur when the epithelial layer of the cornea does not adhere properly to the underlying basement membrane, leading to painful episodes of tearing, redness, and heightened sensitivity to light. Some patients may also experience fluctuating vision throughout the day, with more clear vision upon waking up and gradual blurring as the day progresses.
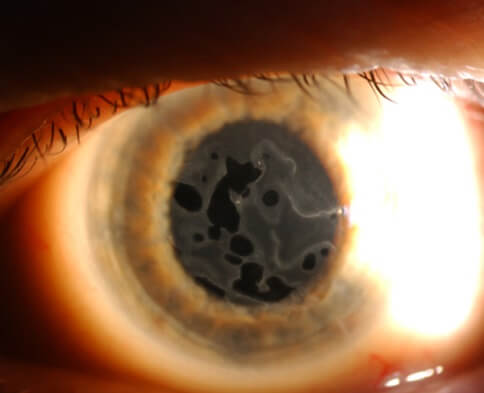
How to Diagnose Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy
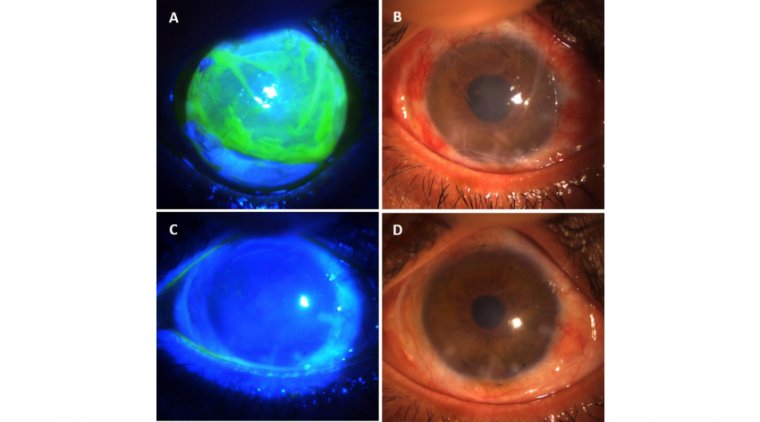
When it comes to diagnosis, a detailed eye examination by a trained eye care professional is crucial. Techniques such as a slit-lamp examination can allow an ophthalmologist to observe any irregularities or abnormalities in the cornea. Advanced imaging techniques like corneal topography, which maps the surface of the cornea, can also assist in some cases.
A key factor in managing ABMD effectively is early detection. Regular eye examinations become increasingly important, particularly for those with a family history of corneal dystrophy. The sooner we can identify the presence of ABMD, the better we can guide patients through the most effective treatment options and ensure that their vision is preserved to the best possible extent.
Treatment Options for Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy
Treatment for Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy (ABMD) is primarily focused on managing symptoms, preventing recurrent corneal erosions, and maintaining quality vision. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and the impact on the individual's daily activities.
For milder cases, the initial treatment often involves the use of lubricating eye drops or ointments. These can help soothe the gritty feeling in the eye and prevent dryness, a common trigger for corneal erosions. Also, lubricants can provide temporary relief from blurred vision and light sensitivity, both common symptoms of ABMD.
For those who experience recurrent erosions or more significant vision loss, more advanced therapeutic interventions may be considered. These include techniques like phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK), a laser procedure that smoothens the cornea's surface, reducing the risk of future erosions and improving visual clarity.
Corneal epithelial debridement, another potential treatment option, involves the physical removal of the affected corneal cells and can be combined with a diamond burr polishing of the Bowman's membrane to further decrease the recurrence of corneal erosions.
In some cases, therapeutic contact lenses can also be a helpful tool. These lenses provide a protective layer over the cornea, helping to prevent erosions and facilitating corneal healing.
Regardless of the treatment modality chosen, the ultimate goal is to customize the plan based on the patient's unique needs. Consulting with an eye care professional is crucial to discuss these options, understand potential risks and benefits, and choose a path that offers the most promising outcomes for the individual's eye health and vision. In ABMD management, personalized care, ongoing monitoring, and open dialogue with your eye care specialist are all essential pieces of the puzzle.
Lifestyle Tips and Self-Care for Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy
Living with Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy (ABMD) can be challenging, but there are practical steps you can take to alleviate symptoms and protect your vision. Prioritizing good eye hygiene is paramount. This includes avoiding rubbing your eyes, which can further irritate the cornea and trigger erosions. Regularly washing your hands and face and using clean towels can also help prevent infections and irritations.
Protecting your eyes from environmental factors like dust, smoke, and harsh winds is important. Wearing sunglasses outdoors, especially those with 100% UV protection, can provide a shield against excessive UV exposure and airborne irritants.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can indirectly support your eye health. A balanced diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E, omega-3 fatty acids, and zinc can promote eye health. Regular exercise and proper hydration also contribute to overall well-being, which in turn supports the body's ability to heal and fend off diseases.
Lastly, consider your eyes as part of your regular health check-ups. Regular visits to an eye care professional can help detect any changes early and adjust treatment as needed.
Summary
Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy (ABMD) is a common corneal dystrophy that can significantly impact an individual's vision and quality of life. While its causes are primarily linked to genetic predisposition, understanding its symptoms—such as blurred vision and recurrent corneal erosions—can facilitate early detection and effective management.
Treatment options for this eye disorder range from simple measures like lubricating eye drops to advanced procedures like phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK), depending on the severity of symptoms. Furthermore, lifestyle adjustments and regular eye care can play a significant role in managing ABMD effectively.
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms suggestive of ABMD, or any corneal dystrophy, consulting with an eye care professional is essential. Remember, your vision is invaluable, and taking proactive steps can make all the difference in its preservation.
(1).jpg)