What Is Ocular Hypotony and How to Manage It
| Table of Content |
| Causes of Ocular Hypotony |
| What Are the Symptoms of Ocular Hypotony? |
| Diagnosis of Ocular Hypotony |
| How to Manage Ocular Hypotony |
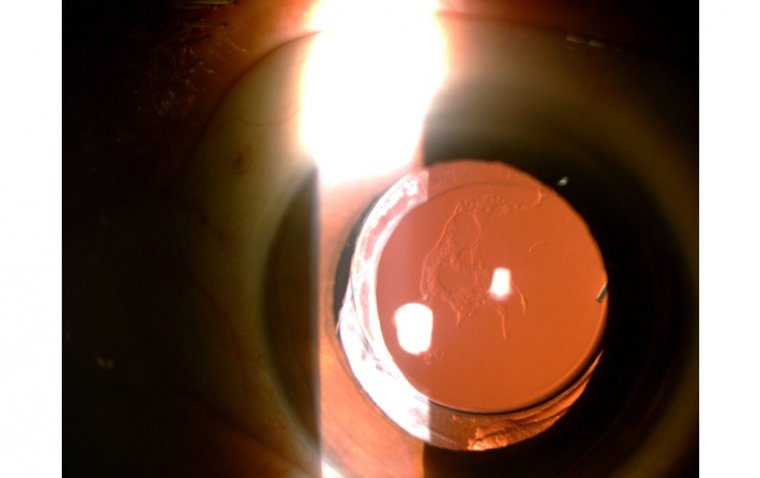
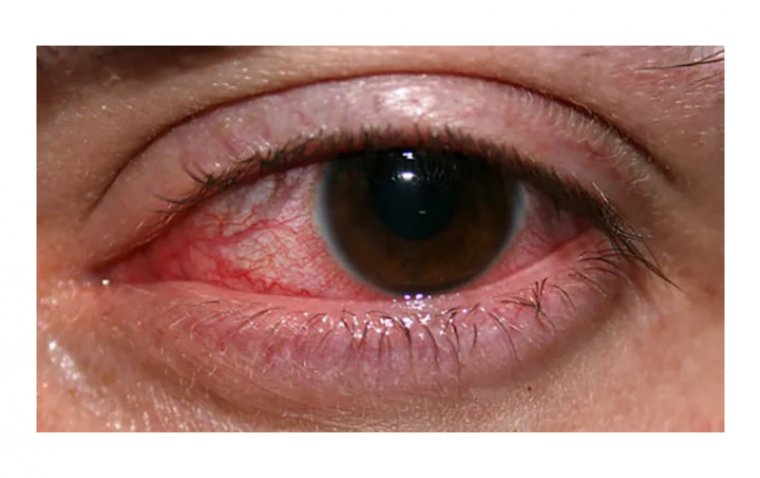
Ocular hypotony, also known as low intraocular pressure, is a condition characterized by abnormally low pressure in the eye. This condition can lead to vision problems, eye pain, and other serious complications if not managed properly. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and management of ocular hypotony.
Causes of Ocular Hypotony
Ocular hypotony can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
| Causes | Description |
|---|---|
| Eye surgery | Eye surgery, particularly glaucoma surgery, can sometimes cause ocular hypotony. |
| Eye trauma | Trauma to the eye can cause damage to the tissues that regulate eye pressure. |
| Inflammation | Inflammation of the eye tissues, such as uveitis, can lead to ocular hypotony. |
| Retinal detachment | If the retina detaches from the eye, it can lead to a decrease in eye pressure. |
What Are the Symptoms of Ocular Hypotony?
The symptoms of ocular hypotony may vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Blurred vision |
Ocular hypotony can cause a decrease in visual acuity and blurry vision. |
| Eye pain | Ocular hypotony can cause eye pain or discomfort, particularly when moving the eye. |
| Photophobia | Individuals with ocular hypotony may become more sensitive to light. |
| Headaches | Some individuals with ocular hypotony may experience headaches. |
Diagnosis of Ocular Hypotony
The diagnosis of ocular hypotony involves a comprehensive eye examination by an eye doctor or ophthalmologist.
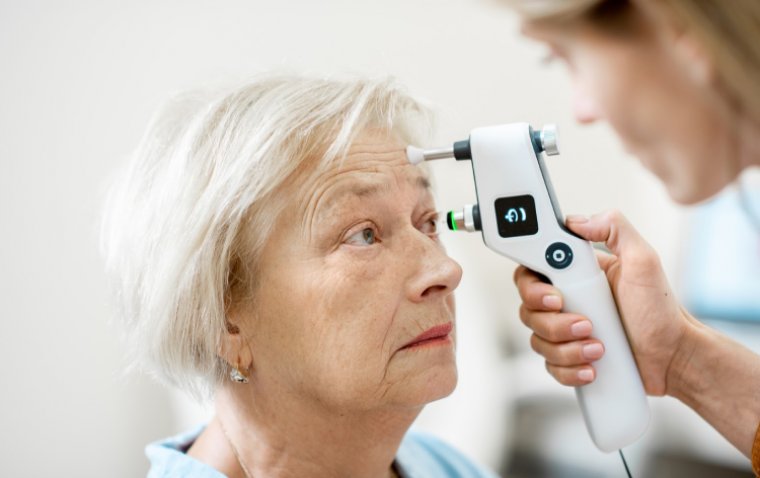
Measurement of Intraocular Pressure (IOP)
IOP is typically measured using a tonometer. In ocular hypotony, the IOP is usually lower than the normal range of 10-21 mmHg.
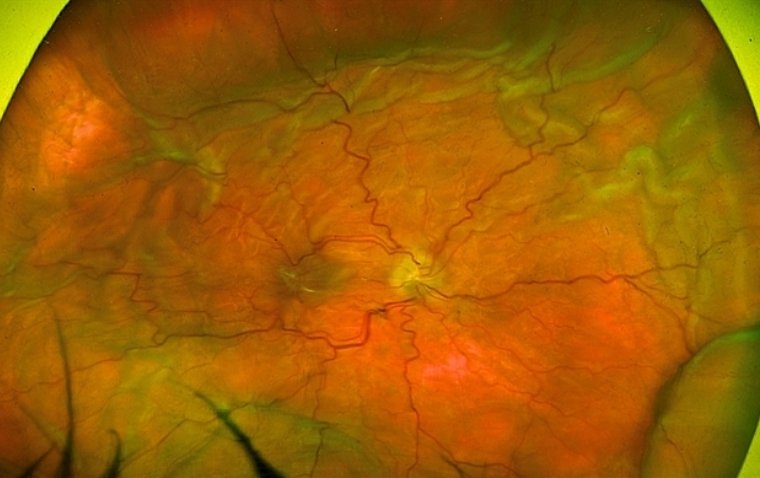
Fundus Examination
Fundus examination involves examining the back of the eye to look for any signs of damage to the optic nerve or retina, which may be a sign of ocular hypotony.
Visual Acuity Testing
Visual acuity testing involves measuring how well a person can see with an eye chart. Ocular hypotony can cause blurred vision and other visual problems, which can be detected through visual acuity testing.
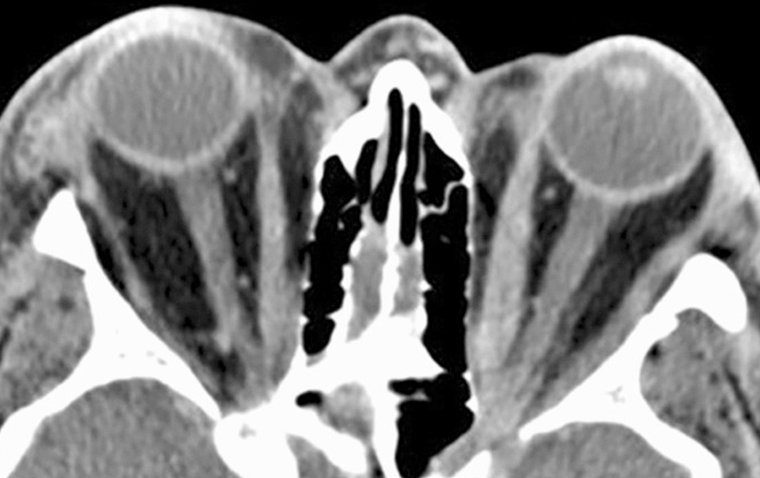
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
Ultrasound biomicroscopy is a non-invasive imaging technique that allows for the visualization of the internal structures of the eye. This can help identify any structural abnormalities that may be causing ocular hypotony.
Gonioscopy
Gonioscopy is a technique that is used to examine the angle where the iris meets the cornea. It can help determine if there is any blockage or damage to the drainage channels of the eye.
How to Manage Ocular Hypotony
The management of ocular hypotony may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common management strategies:
| Management | Description |
|---|---|
| Medications | Eye drops or oral medications may be prescribed to help regulate intraocular pressure. |
| Surgery | In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged eye tissues or to reattach a detached retina. |
| Monitoring |
Regular monitoring of intraocular pressure and vision may be necessary to ensure that the condition does not worsen. |
| Lifestyle modifications |
In some cases, lifestyle modifications such as avoiding activities that may increase eye pressure (such as weightlifting or straining during bowel movements) may be recommended. |
In conclusion, ocular hypotony is a condition that can lead to vision problems and other serious complications if left untreated. If you are experiencing any symptoms of ocular hypotony, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to receive proper diagnosis and management.
(1).jpg)