Understanding Conjunctivochalasis Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide
Overview of Conjunctivochalasis
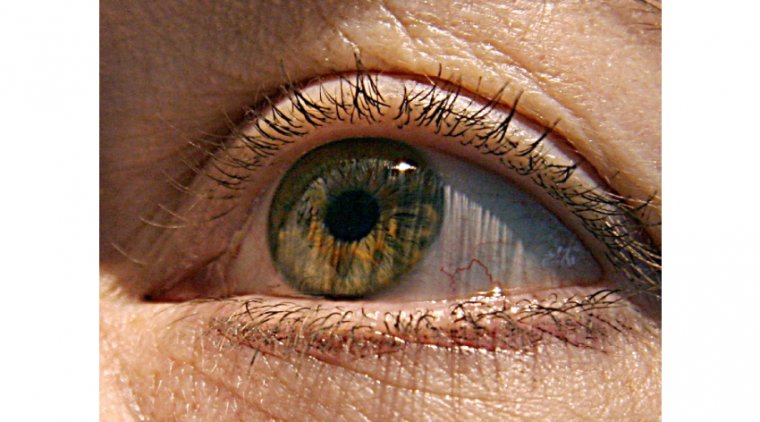
Conjunctivochalasis, though perhaps lesser-known compared to other eye disorders, is a condition that deserves our attention. It manifests as a redundancy of the loose, non-elastic, conjunctival tissue in the eye, often leading to various uncomfortable symptoms.
What is Conjunctivochalasis?
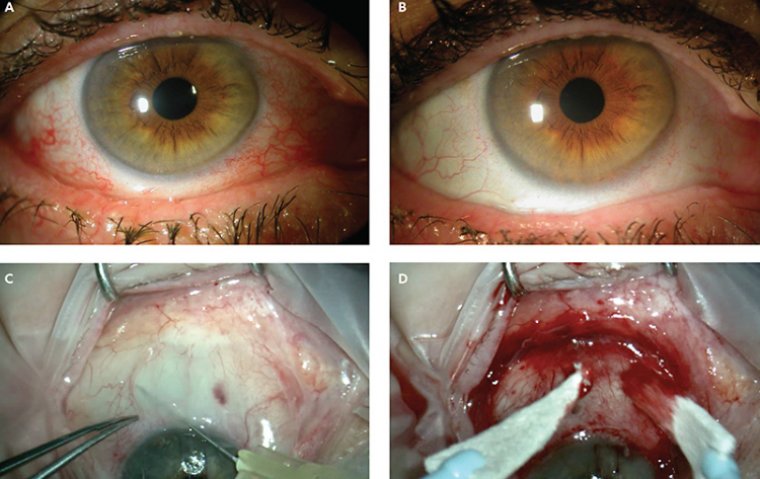
Conjunctivochalasis is a clinical condition characterized by the loosening or redundancy of the conjunctiva, the transparent membrane that covers the white part of the eye. This excess conjunctiva leads to the formation of folds or rolls, predominantly in the lower eyelid, which may interfere with tear flow and eye comfort.
Causes of Conjunctivochalasis
The exact cause of conjunctivochalasis is not entirely understood. However, it is thought to be multifactorial, involving aspects such as aging, inflammation, UV exposure, or ocular surface dryness. It's worth noting that conjunctivochalasis tends to be more common in older adults, suggesting a possible correlation with age-related tissue degeneration.
Symptoms of Conjunctivochalasis
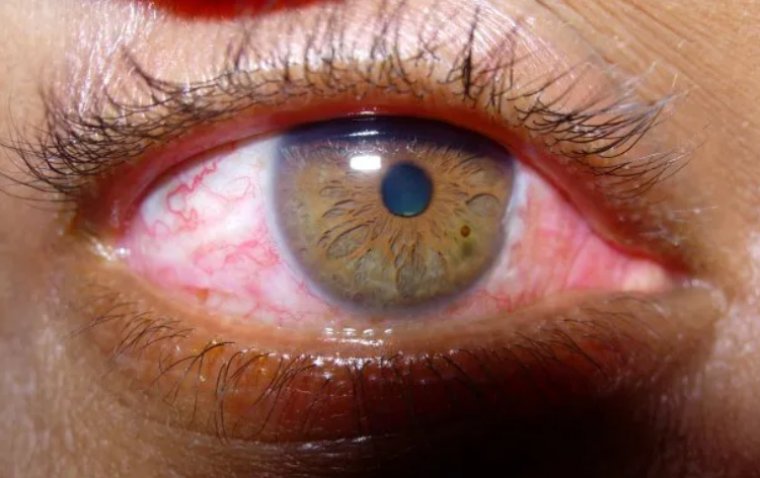
This eye condition presents with a range of symptoms. Patients may experience discomfort or a foreign body sensation in the eye, tearing (epiphora), dryness, redness, and even blurry vision. It is also common for patients to have difficulties wearing contact lenses due to the bulging conjunctival tissue.
.jpg)
How to Diagnose Conjunctivochalasis
The diagnosis of conjunctivochalasis primarily relies on a comprehensive eye examination. The ophthalmologist will carefully evaluate the patient's eyes using slit-lamp biomicroscopy, which provides a magnified view of the eye's structures. The doctor will look for tell-tale signs of conjunctivochalasis, such as redundant folds or rolls of the conjunctiva. In some cases, additional tests like fluorescein staining or a tear film break-up time test may be employed to assess the ocular surface and tear dynamics.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
When managing conjunctivochalasis, the first approach often involves non-surgical treatments, aiming to provide symptomatic relief and improve eye comfort. However, it's crucial to recognize that these options primarily manage the symptoms without addressing the underlying redundancy of the conjunctival tissue.
● Overview of Non-Surgical Approaches: The non-surgical management of conjunctivochalasis largely revolves around alleviating symptoms and improving tear film stability. These treatments aim to minimize discomfort and improve the quality of life for patients.
● Conservative Treatments: The cornerstone of conservative treatment for conjunctivochalasis includes lubricating eye drops and ointments. These help to moisten the ocular surface, alleviate dryness, and provide some relief from the foreign body sensation often associated with this condition. In some cases, doctors may also prescribe topical anti-inflammatory medications to help control any inflammation that may contribute to symptoms.
● Limitations of Non-Surgical Treatments: Despite their role in symptom management, non-surgical treatments do not address the root cause of conjunctivochalasis – the excess conjunctival tissue. While these treatments may offer temporary relief, they are often insufficient for patients with severe conjunctivochalasis or those whose daily life is significantly affected by their symptoms. Furthermore, prolonged use of topical medications can also have side effects, making it an undesirable long-term solution for some patients.
A Look at Conjunctivochalasis Surgery
In more advanced or symptomatic cases of conjunctivochalasis where non-surgical treatments don't provide sufficient relief, surgical intervention may be warranted. These surgeries aim to remove or reposition the redundant conjunctival tissue, thereby rectifying the underlying problem.
Understanding Conjunctivochalasis Surgery
This surgical approach involves the removal or repositioning of excess conjunctival tissue to restore normal eye anatomy and improve tear flow. It's usually performed as an outpatient procedure under local anesthesia. The objective of the surgery is not only to alleviate the symptoms but also to prevent potential complications that may arise from untreated severe conjunctivochalasis.
1. Surgical Techniques
Several techniques can be employed in conjunctivochalasis surgery. The choice depends on the severity of the condition, the patient's overall health, and the surgeon's preference. One common method is conjunctival excision, where the excess tissue is surgically removed. Another technique is conjunctival plication, where the loose conjunctiva is folded and sutured to reduce redundancy. Additionally, amniotic membrane transplantation may be used in more severe cases or when significant ocular surface inflammation is present. This procedure involves grafting amniotic tissue onto the affected area, which aids in healing and reduces inflammation.
2. Benefits of Surgery
Surgical management of conjunctivochalasis can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve patients' quality of life. By addressing the root cause of the issue, it provides a more definitive and long-term solution compared to conservative treatments. Surgery can reduce symptoms like dryness, tearing, and foreign body sensation, and even improve vision in some patients.
3. Possible Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, conjunctivochalasis surgery carries certain risks. These may include bleeding, infection, scarring, or complications related to anesthesia. While relatively rare, there can also be cases of recurrence, where the conjunctival redundancy reappears over time. Furthermore, while most patients experience symptom improvement post-surgery, it's important to understand that the outcomes can vary, and complete symptom resolution is not guaranteed.
4. Preparing for Surgery
Entering the operating room may seem daunting, but with proper preparation and understanding of the process, patients can face the procedure with confidence.
Here's a look at the steps involved in getting ready for conjunctivochalasis surgery and what one can expect before, during, and after the procedure.
- Pre-Operative Preparations: In the lead-up to surgery, the patient will undergo several pre-operative assessments. These may include a thorough medical evaluation to ensure the patient is fit for the surgery, a detailed eye examination, and laboratory tests as needed. It is also a time to discuss any medications the patient is currently taking, as some may need to be adjusted or stopped temporarily. Lifestyle adjustments, such as refraining from smoking or alcohol consumption, may also be recommended to improve surgical outcomes and aid in post-operative recovery.
- Understanding the Process: Knowledge can alleviate many fears. Before surgery, the surgeon will explain the procedure in detail - what will be done, how long it will take, and what kind of anesthesia will be used. This discussion is also an opportunity to clarify any doubts or concerns the patient may have about the procedure.
- The Day of the Surgery: On the day of the surgery, it's important to arrive at the hospital or surgery center well-rested and on time. The patient should follow all the pre-operative instructions given by the surgical team, such as fasting guidelines if required.
- Post-Operative Expectations: After surgery, some eye discomfort, tearing, or mild swelling is normal. These usually subside within a few days. The patient will be given specific instructions regarding eye care, activity restrictions, and signs of complications to watch out for.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular post-operative check-ups are crucial. They allow the surgeon to monitor the healing process, evaluate the success of the surgery, and manage any complications promptly. It is essential for the patient to follow the surgeon's instructions diligently and attend all follow-up appointments.
Recovery and Post-operative Care
Recovery after conjunctivochalasis surgery is a crucial phase, and it's the patient's commitment to proper post-operative care that can make a significant difference in the outcome. Here's what you need to know about the healing journey post-surgery.
● Understanding the Recovery Process: After the surgery, the eye will need time to heal. This recovery period may last a few weeks, and it's common for patients to experience some discomfort, redness, and mild swelling in the early days following the procedure. These symptoms generally resolve gradually as the eye heals.
● Managing Post-Operative Symptoms: Temporary blurred vision, tearing, or a feeling of something in the eye (foreign body sensation) are also common post-operative symptoms. These can be managed with the help of prescribed pain relievers and eye drops. Cold compresses can also help alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling.
● Post-Operative Eye Care: Adhering to the post-operative care instructions is crucial for a successful recovery. This includes regularly using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation, protecting the eye from injury, avoiding rubbing the eyes, and refraining from activities that strain the eyes, such as reading or screen time, for a few days post-surgery.
● Recovery Timeline: The timeline for recovery can vary depending on the individual's overall health, the severity of the condition, and the specific surgical technique used. However, most patients start noticing an improvement in symptoms within a few weeks after the surgery. It's essential to understand that complete healing and symptom resolution may take a bit longer, sometimes several weeks to months.
To Conclude…
Conjunctivochalasis, while a persistent and discomforting eye condition, is no longer a formidable adversary thanks to advanced surgical interventions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic approaches aids in early detection and intervention. Furthermore, appreciating the benefits, risks, and procedure of conjunctivochalasis surgery empowers patients, fostering informed decision-making.
Non-surgical options, though often a first line of defense, might not always provide sufficient relief, making surgical intervention a necessary consideration. The surgery, though it might appear challenging, can often herald a significant improvement in patients' ocular health and their quality of life.
Preparation for surgery is a step-wise process, involving physical readiness and understanding of the procedure. Post-operatively, commitment to the recovery process and strict adherence to prescribed eye care can further enhance the surgical outcome.
In essence, conjunctivochalasis surgery, followed by diligent aftercare, paves the way to reclaiming a life unhindered by eye discomfort. It highlights the resilience of modern ophthalmology in its relentless pursuit to safeguard the precious gift of sight. As patients, clinicians, and caregivers, our joint efforts on this journey can ensure a smooth sail from the shadows of conjunctivochalasis into the clarity of better vision.
(1).jpg)