The Importance of Selenium in Maintaining Eye Health and Vision
Selenium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and wellness, particularly in regards to eye health and thyroid eye disease.
One of the main ways that selenium contributes to eye health is by acting as an antioxidant. Antioxidants are substances that protect the body from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are molecules that can damage cells, leading to inflammation and disease. Selenium helps to neutralize free radicals, preventing them from causing harm to the eyes.
Furthermore, the human body requires selenium for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland and the production of the antioxidant enzyme, glutathione peroxidase.
The Role of Selenium in Managing Symptoms of Thyroid Eye Disease
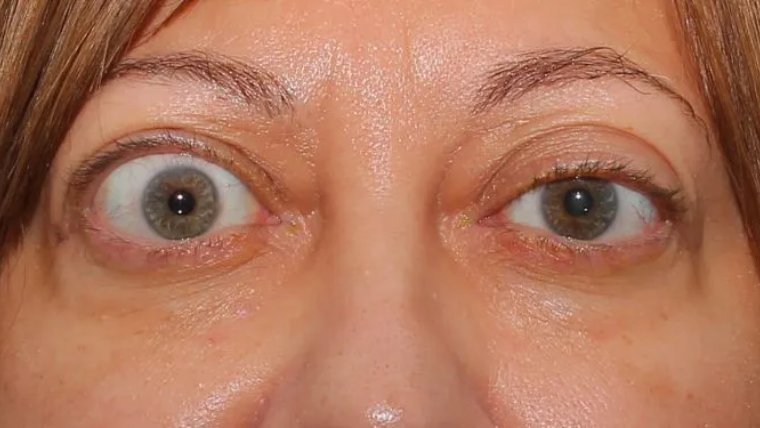
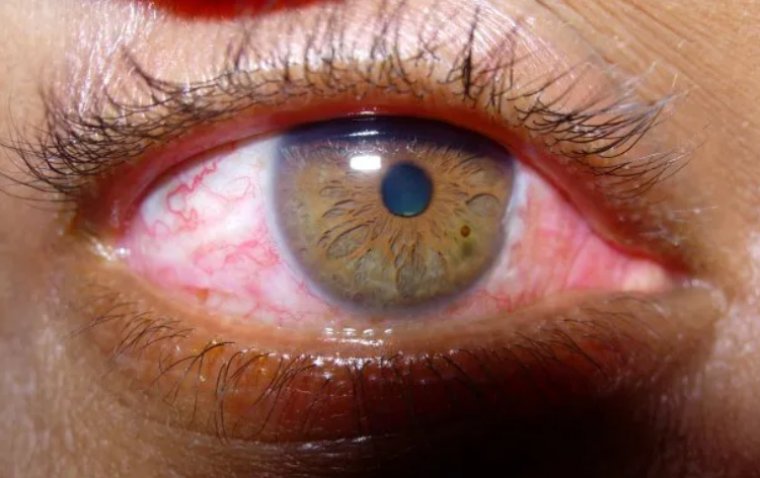
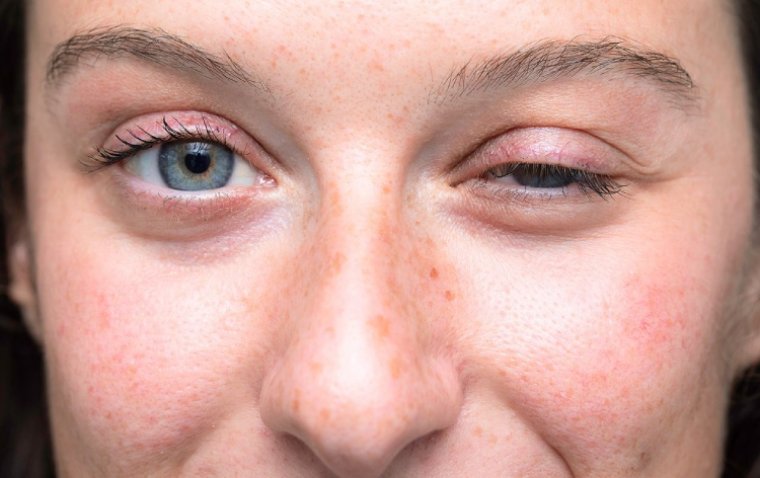
Thyroid eye disease, also known as Graves' orbitopathy, is a condition that occurs as a result of an overactive thyroid gland. It causes inflammation and swelling of the muscles and tissues surrounding the eyes, leading to symptoms such as bulging eyes, double vision, and dry eyes. Studies have shown that individuals with thyroid eye disease have lower levels of selenium in their blood compared to those without the condition. Supplementation with selenium has been found to reduce the severity of symptoms and improve the overall quality of life in those with thyroid eye disease.
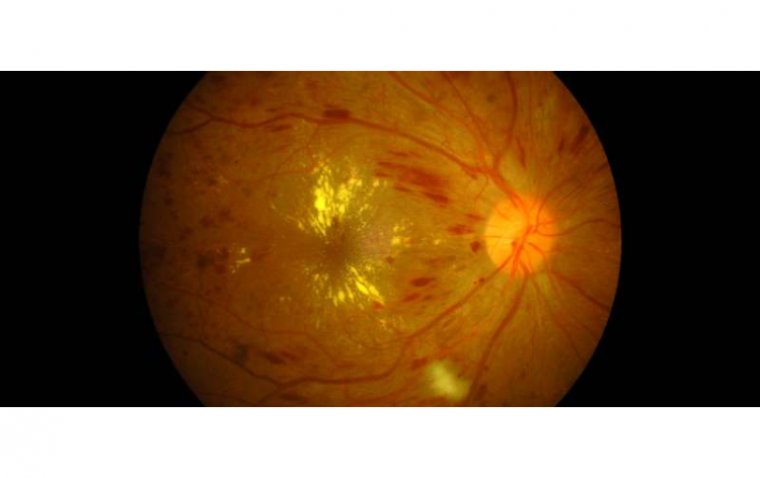
Selenium is also essential for maintaining the health of the retina, the part of the eye that detects light and sends signals to the brain. The retina contains high levels of selenium, and research has shown that low levels of selenium can lead to damage in the retina, increasing the risk of eye disorders such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and cataracts – two of the leading causes of blindness.
In addition to its role in eye health, selenium also has a number of other benefits. It supports the immune system, helps to regulate thyroid function, and may even have anti-cancer properties.
Where Is Selenium Found?
In terms of food sources, selenium can be found in a variety of different types of food, including meats, seafood, eggs, dairy products, and some types of nuts and seeds. Some of the best food sources of selenium include Brazil nuts, tuna, shrimp, and sunflower seeds. Whole grains, such as brown rice and barley, also contain selenium. However, the selenium content of foods can vary depending on the selenium content of the soil in which they were grown or raised.
Selenium is also found in water, with the amount of selenium in water sources varying depending on the location. Some groundwater sources contain high levels of selenium, while others contain very little. Selenium can also be found in some types of seafood, such as tuna, halibut, and sardines.
In terms of supplement form, selenium supplements come in different forms such as tablets, capsules, and liquids. It is important to note that Selenium is toxic in high doses. The recommended daily dose for adults is 55 micrograms for adults. Excessive intake can lead to hair loss, skin rash, and nervous system problems. It is always recommended to consult a healthcare professional before taking any new supplement.I
In conclusion, selenium plays a crucial role in maintaining eye health and can be particularly beneficial for individuals with thyroid eye disease. Incorporating selenium-rich foods into the diet or consulting a healthcare professional about supplement options can help to ensure adequate intake of this essential mineral.
(1).jpg)