The Contagious Conjunctivitis: Understanding Madras Eye Disease
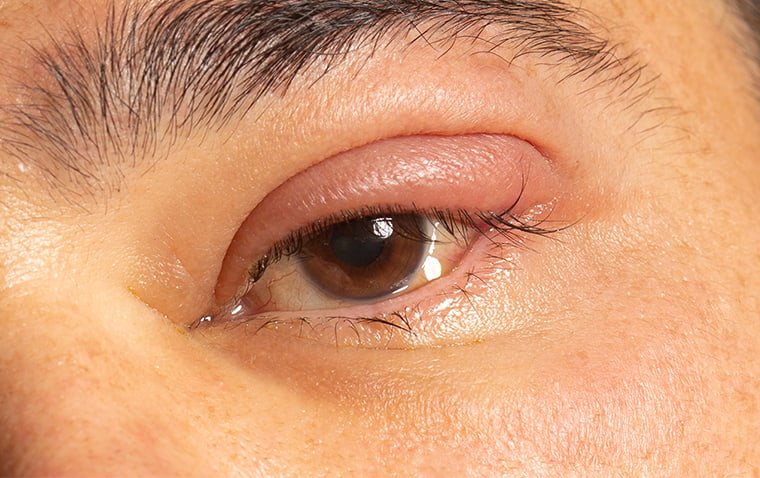
Madras eye disease, also known as conjunctivitis, is a common eye condition characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the clear membrane covering the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids. It is a highly contagious condition that spreads easily from one person to another.
Causes of Madras Eye Disease
Madras eye disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
● Viral infections: The most common cause of conjunctivitis is a viral infection, such as the adenovirus.
● Bacterial infections: Bacterial conjunctivitis can be caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pneumoniae.
● Allergic reactions: Conjunctivitis can also be caused by an allergic reaction to substances such as pollen, pet dander, or dust mites.
● Chemical irritants: Exposure to irritants such as chlorine or other chemicals can also cause conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of Madras Eye Disease
Patients with Madras eye disease typically experience the following symptoms:
● Redness and swelling of the affected eye
● Itching and burning sensation
● Discharge from the affected eye, which may be clear or yellowish
● Increased tearing
● Light sensitivity
● Blurred vision
Diagnosis and Treatment of Madras Eye Disease
Diagnosis of Madras eye disease is made through a comprehensive eye examination, including slit-lamp biomicroscopy, corneal thickness measurement, and laboratory tests.
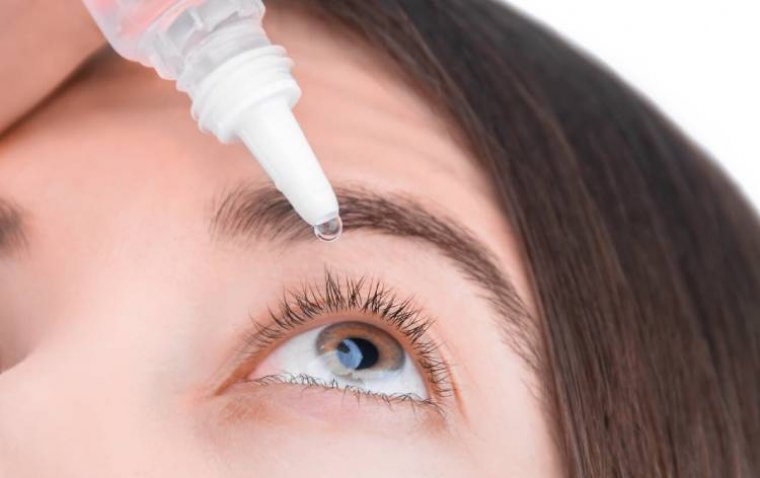
Treatment for Madras eye disease depends on the underlying cause, but typically involves:
● Antibiotic eye drops or ointment for bacterial conjunctivitis
● Anti-inflammatory drops for viral conjunctivitis
● Allergy medication for allergic conjunctivitis
● Avoiding exposure to irritants for conjunctivitis caused by chemical irritants.
How Long Does It Take to Treat Madras Eye Disease?
For viral conjunctivitis, symptoms usually resolve within 7 to 14 days, although the virus may remain in the body for several weeks. For bacterial conjunctivitis, treatment with antibiotics can help relieve symptoms in 2 to 5 days, and complete resolution may take up to 2 weeks. Allergic conjunctivitis may resolve within a few days to several weeks, depending on the allergen and the individual's immune system.
How to Prevent Madras Eye Disease from Spreading?
To prevent the spread of Madras eye disease, it is important to follow these guidelines:
● Wash hands frequently with soap and water
● Avoid touching the eyes and face
● Do not share towels, eye drops, or makeup
● Dispose of tissues properly
● Avoid close contact with infected individuals
● Practice good hygiene by keeping the eye area clean and free of discharge.
In conclusion, Madras eye disease (conjunctivitis) is a common and highly contagious eye condition that can cause redness, swelling, and discharge in the affected eye. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help relieve symptoms and prevent the spread of the disease.
(1).jpg)