Cataracts: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
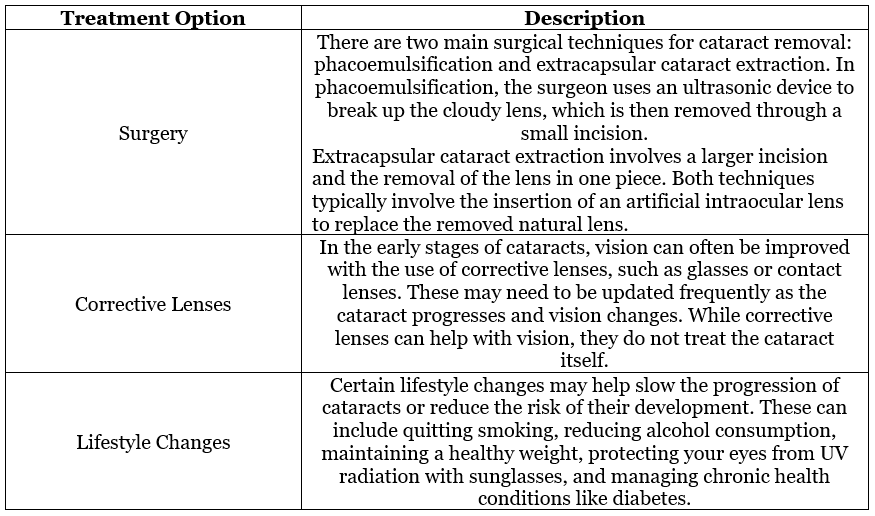
Cataracts are a common eye condition that occurs when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, leading to a decrease in vision. The lens, which is normally clear, helps focus light onto the retina at the back of the eye to produce clear images. As cataracts develop, the lens loses its transparency, causing vision to become blurry or dim.
Cataracts are a widespread issue, affecting millions of people worldwide. They are a leading cause of blindness, especially in older adults. Age is the primary risk factor, with over half of individuals aged 80 or older experiencing some degree of cataract formation. Other risk factors include diabetes, smoking, obesity, prolonged exposure to sunlight, eye injuries, and a family history of cataracts.
What Causes Cataracts?
The most common cause of cataracts is aging. As people age, the proteins in the lens of the eye can clump together, leading to a clouding of the lens. This process is gradual and can occur in one or both eyes, resulting in the progressive decline of vision over time.
Other factors that can contribute to cataracts development:
1. Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can increase the risk of developing cataracts.
2. UV radiation: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can damage the lens of the eye and contribute to the formation of cataracts.
3. Health conditions: Medical conditions, such as diabetes, can lead to cataracts. High blood sugar levels can cause changes in the lens of the eye, increasing the risk of cataract development.
4. Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can also increase the risk of cataracts.
Symptoms of Cataracts
Blurred or distorted vision One of the most common symptoms of cataracts is blurry or distorted vision, which can make it difficult to read, drive, or recognize faces. This can occur in one or both eyes, and the degree of blurriness may vary.
Sensitivity to light and glare Cataracts can cause increased sensitivity to light, making it uncomfortable to be in bright environments. Glare, or the scattering of light, can also become a problem, especially when looking at oncoming headlights while driving at night.
Difficulty seeing at night as cataracts progress, they can make it harder to see in low-light conditions. This can result in difficulty navigating at night, both indoors and outdoors.
Diagnosing Cataracts
Eye exams and visual acuity tests: A comprehensive eye exam is essential for diagnosing cataracts. During the exam, an ophthalmologist or optometrist will conduct a visual acuity test, which measures the sharpness of your vision. This test typically involves reading letters on a chart at varying distances to determine how well you can see.
Dilated eye exams and lens exams: During a dilated eye exam, the eye care professional will use special drops to dilate, or widen, your pupils. This allows them to examine the retina and optic nerve more easily, as well as the lens, where cataracts form. The doctor will use a slit-lamp microscope to evaluate the lens for signs of cloudiness or other abnormalities.
Other diagnostic tests that may be used in some cases, additional tests may be performed to assess the severity of the cataract and its impact on your vision. These tests may include:
1. Contrast sensitivity test: This test measures how well you can distinguish between different levels of contrast, which can be affected by cataracts.
2. Glare test: A glare test evaluates your ability to see in the presence of bright light, which can be difficult for people with cataracts.
3. Potential acuity meter (PAM) test: This test estimates how well you might see after cataract surgery by projecting an image directly onto your retina, bypassing the cloudy lens.
4. Optical coherence tomography (OCT): This noninvasive imaging test provides detailed images of the retina and can help assess the impact of cataracts on your vision.
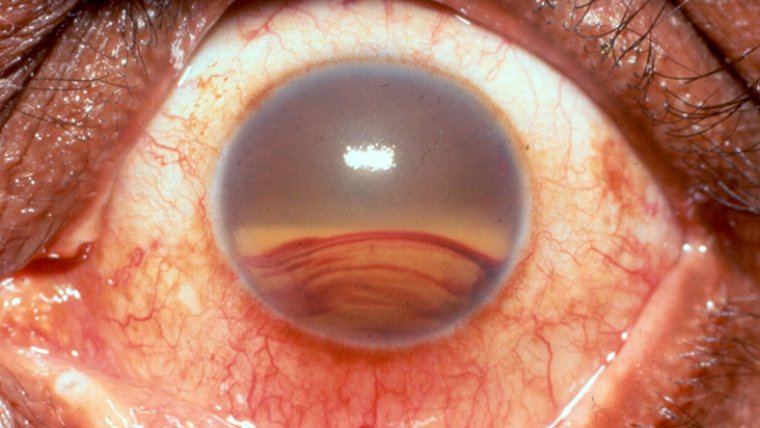
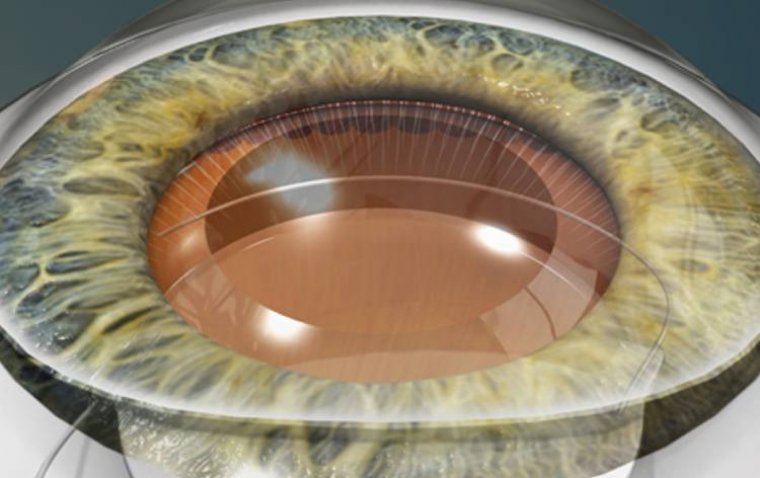
Treatment Options for Cataracts
Do Eye Drops that Dissolve Cataracts Exist?
The existence of eye drops that can effectively dissolve cataracts is a topic of ongoing research and development. While there have been claims and studies suggesting the potential for such eye drops, currently, there is no widely accepted or FDA-approved eye drop specifically designed to dissolve cataracts.
Recovery and Managing Cataracts
Recovery from cataract surgery is generally quick and uncomplicated. Patients may experience mild discomfort, itching, or sensitivity to light for a few days following the procedure. Most people can return to their daily activities within 24 to 48 hours.
Complete recovery, including vision stabilization, usually occurs within a few weeks. It is important to follow your eye care professional's instructions regarding post-operative care, such as using prescribed eye drops and avoiding activities that may strain your eyes.
Regular eye exams are essential for monitoring the progression of cataracts and maintaining optimal eye health. Early detection can help you and your eye care professional develop a management plan that addresses your specific needs. If you have cataracts, it is crucial to have your vision checked regularly to ensure that your corrective lenses remain up-to-date and that any changes in your vision are promptly addressed.
Lifestyle Changes That May Help Improve Vision and Manage Symptoms
In addition to regular eye exams, making certain lifestyle changes can help improve your vision and manage cataract symptoms. These changes may include:
1. Adjusting lighting: Ensure that your living and workspaces have adequate lighting to reduce eye strain and make it easier to see.
2. Using magnifying devices: Magnifying glasses, large-print books, or electronic devices with adjustable font sizes can make reading and other close-up tasks more manageable.
3. Limiting screen time: Taking regular breaks from screens, such as computers and smartphones, can help reduce eye strain and discomfort.
4. Wearing sunglasses: Protect your eyes from harmful UV radiation by wearing sunglasses with 100% UVA and UVB protection when outdoors.
5. Eating a balanced diet: A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can support eye health and may help slow the progression of cataracts. Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
By combining regular eye care, appropriate treatment options, and supportive lifestyle changes, you can better manage cataracts and maintain your vision.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cataracts are a common eye condition characterized by the clouding of the eye's lens, leading to a decrease in vision. Aging is the primary cause of cataracts, but other factors such as certain medications, UV radiation, and health conditions like diabetes can also contribute to their development. Symptoms of cataracts include blurred or distorted vision, sensitivity to light and glare, and difficulty seeing at night.
Diagnosing cataracts typically involves comprehensive eye exams, visual acuity tests, and dilated eye exams. Treatment options for cataracts include surgery, corrective lenses, and lifestyle changes to slow the progression of the condition. Recovery from cataract surgery is generally quick and uncomplicated, but managing the condition requires regular eye exams and monitoring.
If you are experiencing symptoms of cataracts, it is essential to seek professional advice and support from an eye care professional. Early detection and proper management can help maintain your vision and improve your quality of life.
(1).jpg)