Sudden Vision Loss: A Medical Emergency
Sudden vision loss is a serious medical condition that can be caused by a variety of underlying factors. It can be a symptom of a number of serious conditions, including retinal detachment, stroke, and even brain tumors. Understanding the causes of sudden vision loss is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
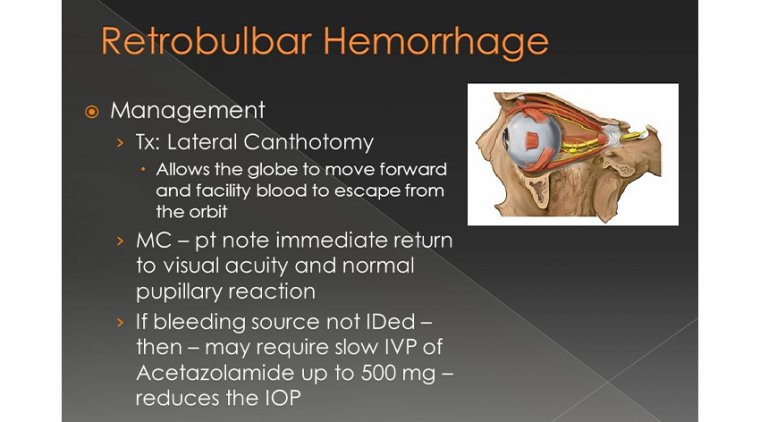
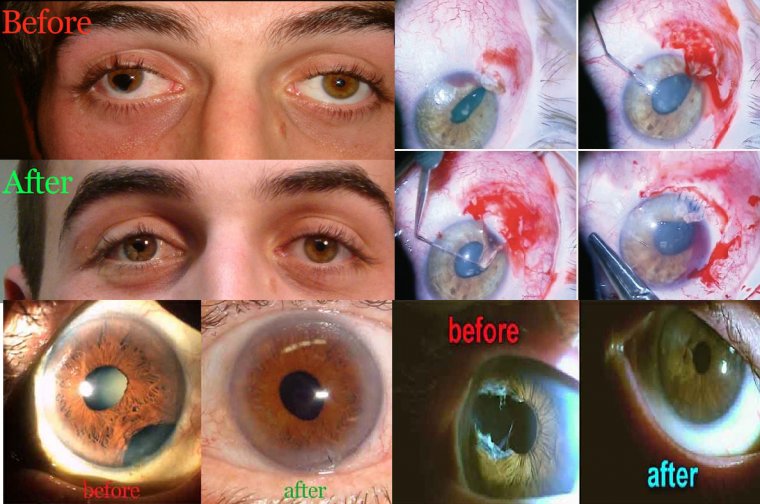
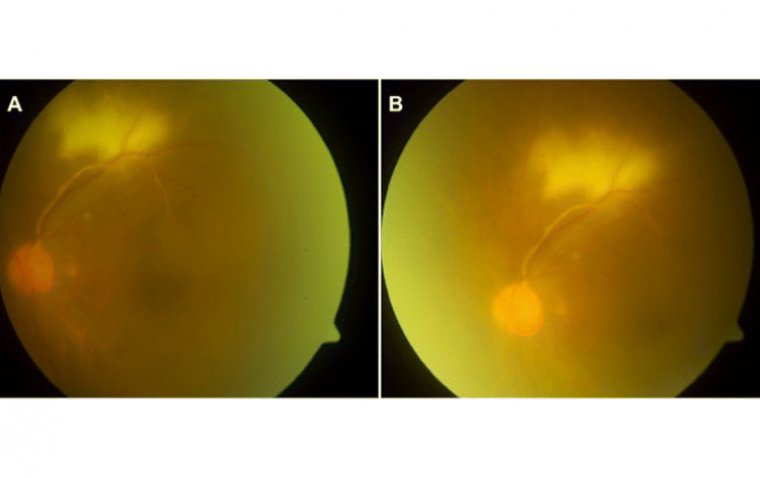
One of the most common causes of sudden vision loss is retinal detachment. The retina is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that sends visual signals to the brain. If the retina becomes detached, it can no longer function properly, leading to sudden vision loss. Retinal detachment can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, certain medical conditions, and even certain eye surgeries.
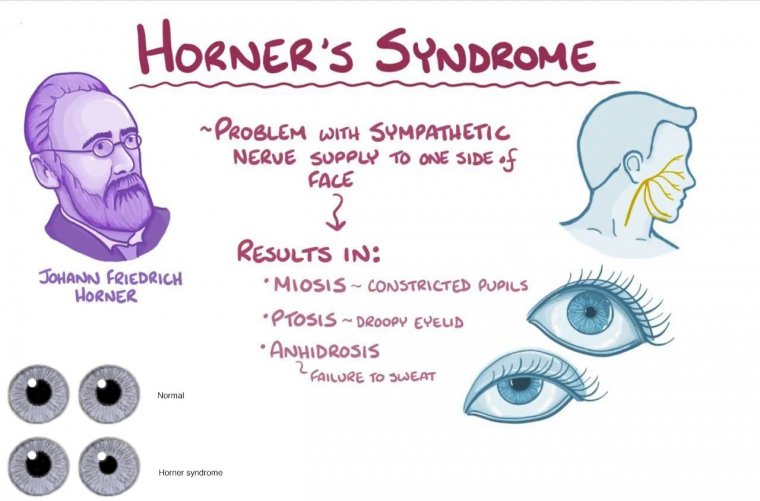
Another common cause of sudden vision loss is a stroke. A stroke occurs when the blood flow to the brain is interrupted, depriving brain cells of oxygen and nutrients. This can lead to vision loss in one or both eyes. Strokes can be caused by a variety of factors, including high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes.
Brain tumors can also cause sudden vision loss. Tumors can press on the optic nerve, which carries visual signals from the eye to the brain. This can lead to vision loss in one or both eyes. Brain tumors can be benign or malignant and can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics and exposure to certain toxins.
Other causes of sudden vision loss include optic neuritis, which is inflammation of the optic nerve, and giant cell arteritis, which is an inflammation of the blood vessels in the head.
It's important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience sudden vision loss. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent permanent vision loss and improve your overall outcome. Your healthcare provider will perform a thorough examination and may order imaging tests such as MRI, CT scan, and an eye examination, to help determine the cause of your vision loss.
Sudden Vision Loss in One Eye
The primary cause of sudden vision loss in one eye is high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. High blood pressure is a condition in which the force of blood against the walls of the blood vessels is too high. This extra force can damage the blood vessels in the eye, leading to vision loss.
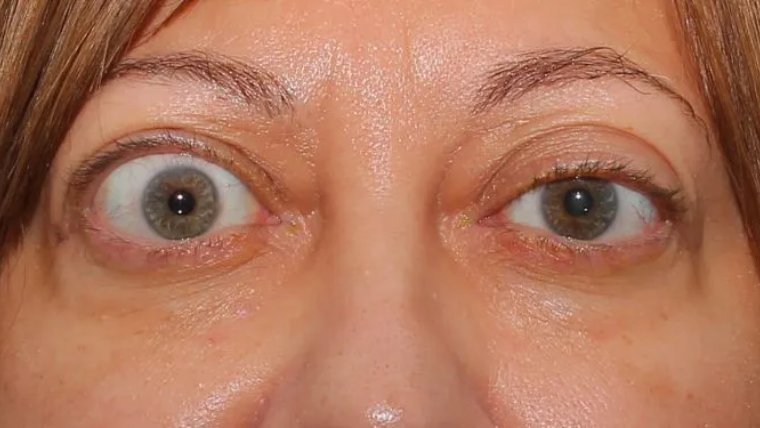
Symptoms of sudden vision loss in one eye include blurred vision, loss of peripheral vision, and the appearance of a dark spot or "shadow" in the affected eye. These symptoms can occur suddenly and without warning. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
.jpg)
Risk Factors for Sudden Vision Loss
● Age: As we get older, the risk of developing certain eye conditions such as age-related macular degeneration, cataracts, and diabetic retinopathy increases. These conditions can lead to sudden vision loss. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a degenerative disorder of the retina that affects older adults and can cause a loss of central vision.
● Medical conditions: People with diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol are at an increased risk of developing eye conditions that can lead to sudden vision loss. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy, which can cause sudden vision loss. High blood pressure and high cholesterol can also damage the blood vessels in the eye, leading to sudden vision loss.
● Genetics: Some eye conditions that can lead to sudden vision loss, such as retinal detachment, are more common in certain families. If you have a family history of eye conditions that can cause sudden vision loss, you may be at a higher risk.
● Trauma: Injury or trauma to the eye, such as a blow to the head, can lead to sudden vision loss. Additionally, certain eye surgeries, such as cataract surgery, can also increase the risk of sudden vision loss.
● Certain medications: Certain medications, such as blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs, can increase the risk of sudden vision loss.
● Toxins and environmental factors: Exposure to certain toxins and environmental factors, such as pesticides and pollutants, can increase the risk of sudden vision loss.
How Is Sudden Vision Loss Treated?
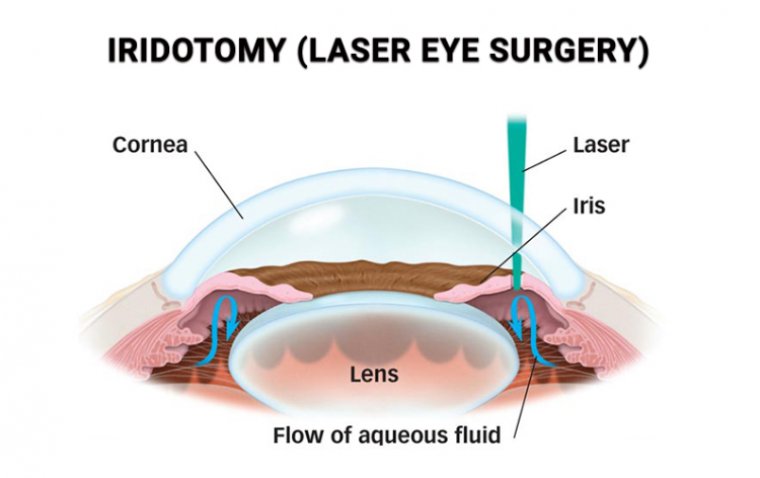
Treatment for sudden vision loss will depend on the underlying cause. For example, retinal detachment may require surgery, while a stroke may require medication or other types of therapy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sudden vision loss is a serious medical condition that can be caused by a variety of underlying factors. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing permanent vision loss. If you experience sudden vision loss in one eye, seek medical attention immediately. Don't ignore or delay seeking professional help, as it can lead to permanent vision loss.
(1).jpg)