How Photopsia Occur and What Are the Dangers?
Photopsia Definition
Briefly, a photopsia is a flash or light floating in your eye. They appear to be shiny and luminous. They can be experienced in one eye or both eyes at the same time. Photopsia can either be temporary or they can be permanent.
How is Photopsia Treatment?
Photopsia is actually a symptom of another underlying cause. Hence, the treatment depends on the underlying cause. There’s not a single treatment. If the patient is experiencing it due to age-related macular degeneration injections of anti-VEGF help. If the cause is optic neuritis, usually the eye improves on its own.
If there’s any damage in the structure of the eye, in the optic nerve, or the brain, photopsia may be permanent.
If the situation gets worse, it indicates that the underlying cause is also getting worse. It’s of great importance to seek medical assistance.
What Are the Symptoms of Photopsia?
Photopsia, i.e. specks in the eyes float as you move your eyes or head. It feels like something is in your field of vision. However, they’re usually inside your eye, optic nerve, or brain that causes you to see these things in your field of vision.
This so-called photopsia are more visible in the dark, as they’re bright and luminous. In some cases where they’re extremely flashed, they may also be noticed during daytime.
When you experience these floaters accompanied by flashes, you should immediately book an appointment with your ophthalmologist.
Below list is some of the symptoms of the condition.
● Flashes and luminous light
● Floating shapes in the field of vision
● Moving dots
● Static
● Twinkling lights
What Are the Causes of Photopsia?
As mentioned earlier, photopsia is not a disorder on its own but a cause of another problem. Some of the example causes of photopsia are listed below.
Age-related macular degeneration is seen in people aged over 50. Macular part of the maculares helps us see clearly what’s in front of us. Photopsia is one of the signals of degeneration.
● Optic neuritis is an inflammation that damages the optic nerve resulting in problems when the images are processed in the brain. The most common cause of it is multiple sclerosis. Some flashes and flickering light in the field of vision.
● Peripheral vitreous detachment can cause serious structural problems as the vitreous humor is the part within the organ that keeps it together. When the gel detaches from the retina it may cause peripheral vision loss. This usually happens as we age but it can also happen spontaneously and when it happens too fast, photopsia may occur.
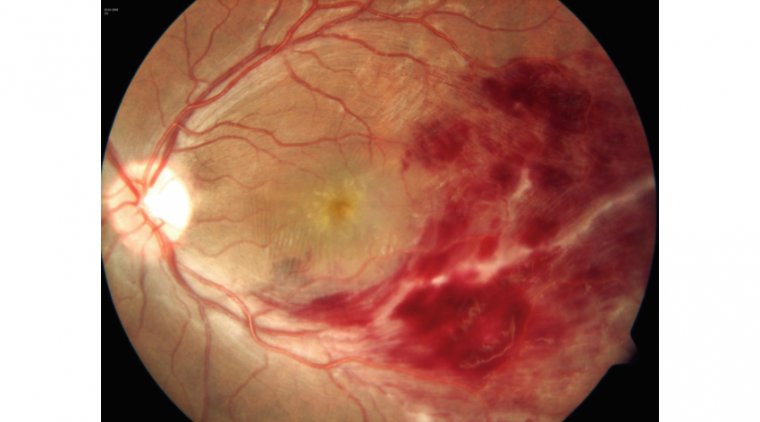
● Retinal detachment can lead to a change in our vision as our retina collects information about the light and transmit that to the brain to convert it into images. Retinal detachment is a serious condition that needs to be treated immediately. Sudden photopsia is one of the indicators of the condition.
● Vertebrobasilar insufficiency is poor blood flow to the back side of the brain, which causes a lot of damage. One of the symptoms of that is the change in the visual field, including photopsia.
What is Migraine Photopsia?
A migraine aura is a wave of activity in the brain. The location of the activity in the brain determines the type of aura. The most common one is visual. Almost all the people who have migraine with aura have this type. A migraine aura that affects your vision is common and its symptoms don’t last very long. You may experience bilateral photopsia, meaning flashes of light, and blind spots. Unfortunately, these symptoms can cause problems when doing Daily activities like reading or driving. A migraine with aura isn't usually considered serious.
Retinal migraine is a rare condition that a person who experienced different symptoms of migraine. Retinal migraine causes repeated rounds of quickly diminished vision or blindness.
Unlike migraine aura, retinal migraine affects only one eye. If you experience photopsia or visual loss in one eye, be sure to seek medical assistance.
(1).jpg)