Emmetropic Eyes: The Gold Standard of Vision
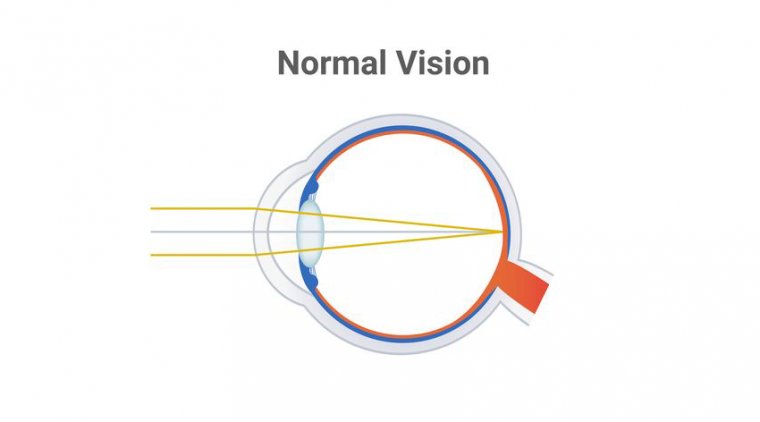
Emmetropia is a term used to describe a healthy eye that is capable of focusing light properly on the retina. It is the ideal state of vision, where the eye is able to produce clear, sharp images without the need for glasses or contact lenses. An emmetropic eye has a cornea with a curvature that is just right to focus light precisely onto the retina, producing a clear, undistorted image.
How to Maintain Emmetropia
Even though emmetropic eyes are considered to be healthy and free from visual defects, they still need to be protected from harmful environmental factors. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun, for example, can cause damage to the retina and increase the risk of cataracts, age-related macular degeneration, and other eye diseases.
To protect your emmetropic eyes, you should take the following precautions:
● Wear sunglasses that offer 100% UV protection when you are outside for extended periods of time.
● Use computer glasses that block harmful blue light when working on a computer or looking at digital devices.
● Get regular eye exams to monitor your eye health and detect any potential problems early.
Does Emmetropia Always Mean that Your Eyes Are Perfectly Healthy?
While emmetropia is a positive indicator of good vision, it is not a guarantee of perfect eye health. There are other factors that can affect the overall health of the eye, such as age-related changes, eye diseases, and other health conditions. For example, an emmetropic eye can still develop cataracts, age-related macular degeneration, or glaucoma.
Terefore, it is important for individuals with emmetropic eyes to have regular eye exams and to take steps to protect their eyes from harmful environmental factors, such as UV rays from the sun and blue light from digital devices.
Difference between Emmetropia and Ametropia
Emmetropia and ametropia are terms used to describe different states of vision. While emmetropia refers to a healthy eye that is capable of focusing light properly, ametropia refers to an eye that has a visual defect and is unable to focus light properly.
There are three main types of ametropia: myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism. In myopia, the eye is too long or the cornea is too curved, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of on it. This results in difficulty seeing objects in the distance. In hyperopia, the eye is too short or the cornea is too flat, causing light to focus behind the retina instead of on it. This results in difficulty seeing objects up close. Astigmatism is a condition where the cornea is misshapen, causing light to focus on multiple points instead of one, resulting in distorted or blurred vision.
In conclusion, emmetropia is the ideal state of vision, but even emmetropic eyes need to be protected from harmful environmental factors. On the other hand, ametropia refers to an eye with a visual defect that results in difficulty seeing objects clearly. By taking proper precautions and getting regular eye exams, you can help maintain your emmetropic eyes and prevent the onset of vision problems.
(1).jpg)