Understanding Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy
What is EBMD?
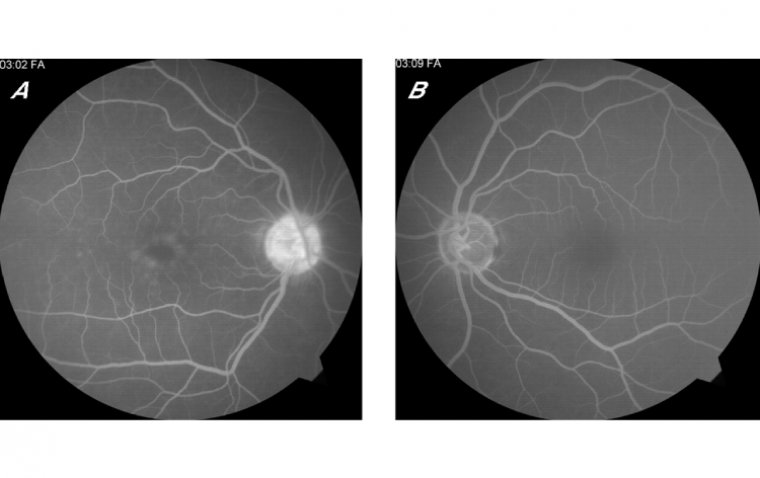
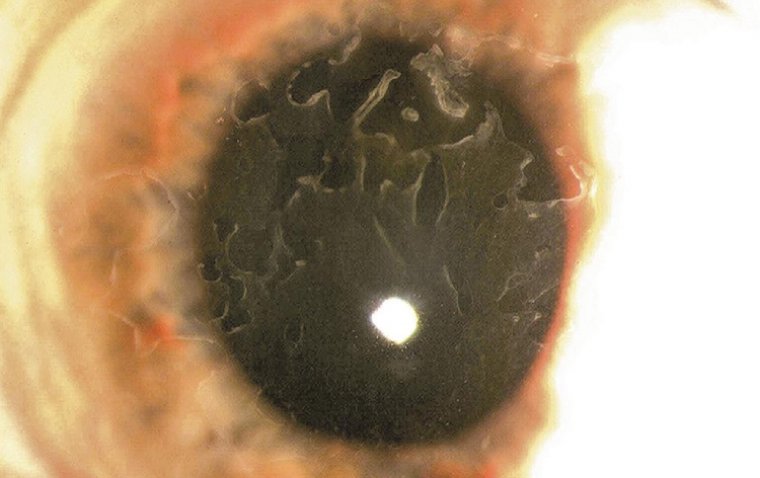
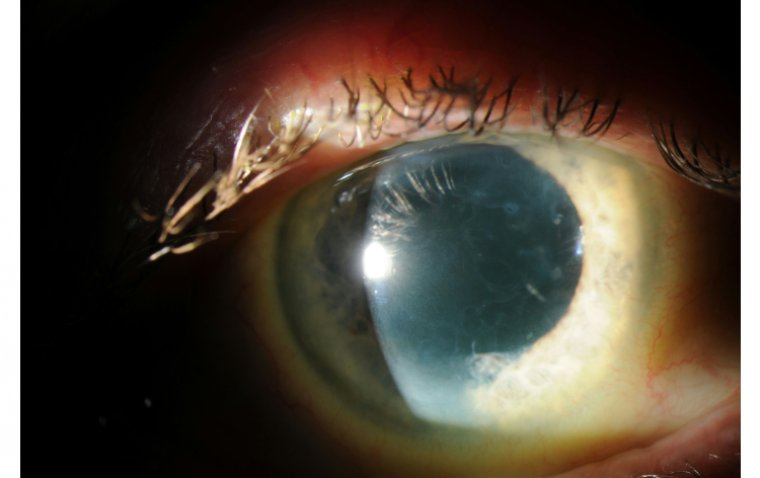
Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD), also known as Map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy, is a common and often asymptomatic corneal disorder. It affects the layer of cells that cover the front of the eye, known as the corneal epithelium. This layer usually is smooth and transparent, allowing light to pass through and focus on the retina. However, in individuals with EBMD, the epithelium can become irregular and thickened, resulting in visual disturbances.
Causes of EBMD
The exact cause of EBMD has yet to be fully understood, but several factors are thought to contribute to its development.
1. Genetic factors: Evidence suggests that EBMD may have a genetic component. Studies have identified mutations in genes involved in the development of the cornea, and these mutations have been linked to the development of EBMD in some individuals. These genetic factors may influence the structure and function of the basement membrane, leading to the irregularities seen in EBMD.
2. Age: EBMD is more common in older individuals, and it is thought that age-related changes in the cornea may contribute to its development. As we age, the basement membrane of the cornea may become less organized, which can lead to irregularity formation.
3. Trauma: In some cases, trauma to the eye may lead to the development of EBMD. This is thought to occur because the trauma can damage the cornea's basement membrane, leading to irregularity formation.
4. Dry eye syndrome: Individuals with dry eye syndrome are more likely to develop EBMD. This is likely because the lack of moisture in the eye can cause the basement membrane to become irregular and more susceptible to damage.
5. Inflammatory conditions: Inflammatory conditions such as rosacea and blepharitis can also contribute to the development of EBMD. These conditions can cause chronic inflammation of the eyelids, which can lead to damage to the basement membrane of the cornea.
6. Environmental factors: Exposure to environmental factors such as ultraviolet radiation, wind, and dust may also contribute to the development of EBMD. These factors can cause damage to the cornea, which can lead to the formation of irregularities in the basement membrane.
Is EBMD Hereditary?
Yes, EBMD is considered to be a hereditary condition. It is often passed down through families and can affect multiple generations. However, not all individuals with a family history of EBMD will develop the condition.
Signs and Symptoms of EBMD
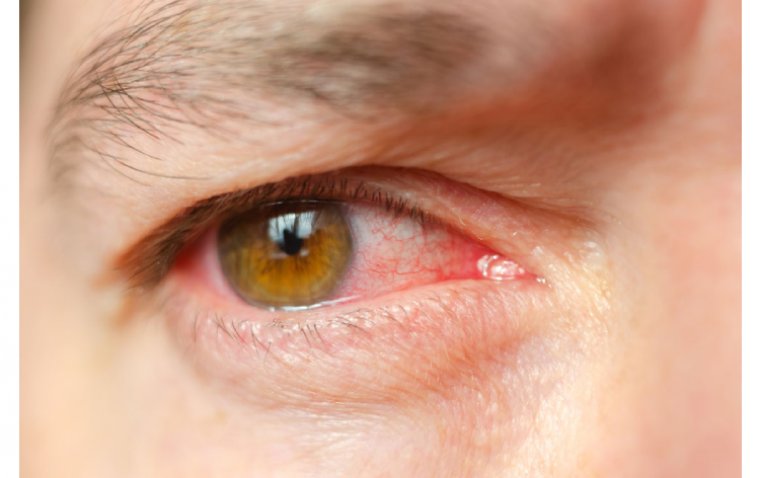
Many individuals with EBMD are asymptomatic and may not realize they have the condition. However, some people may experience the following signs and symptoms:
● Blurred or distorted vision
● Sensitivity to light
● The sensation of a foreign object in the eye
● Dryness and irritation
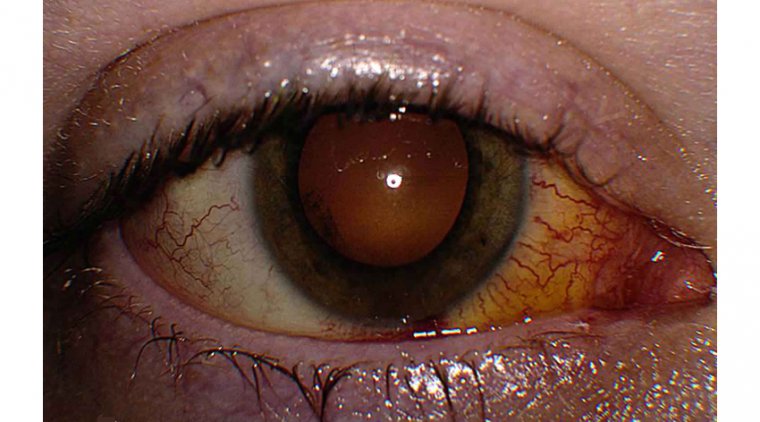
● Epithelial erosions, which can cause pain and discomfort
Can EBMD Lead To Vision Loss?
In most cases, EBMD does not lead to permanent vision loss. However, some individuals may experience recurrent epithelial erosions, which can cause pain and discomfort and may result in cornea scarring. In rare cases, this scarring can lead to visual impairment or even blindness.
How Is EBMD Treated?
Can EBMD Recur After Treatment?
Yes, EBMD can recur after treatment, particularly in individuals with a family history of the condition. Regular follow-up appointments with an ophthalmologist are recommended to monitor the condition and address any recurrent symptoms.
Are There Any Ways To Prevent EBMD?
There is currently no known way to prevent EBMD. However, individuals can reduce their risk of developing symptoms by protecting their eyes from UV light and maintaining good eye health through regular eye exams and proper eye care. Additionally, individuals with a family history of EBMD may benefit from genetic counseling to understand their risk of developing the condition and how it may affect future generations.
In conclusion, epithelial basement membrane dystrophy is a common corneal disorder that affects the layer of cells covering the front of the eye. Although it is often asymptomatic, some individuals may experience blurred vision, sensitivity to light, and other uncomfortable symptoms. While there is no known way to prevent EBMD, it can be managed through conservative treatments and regular follow-ups with an eye doctor. Additionally, individuals with a family history of EBMD may benefit from genetic counseling to better understand their risk of developing the condition.
Author: Dr. Muhammad Saad, Post Graduate Resident at Alshifa Trust Eye Hospital Rawalpindi
(1).jpg)
.PNG)