Amniotic Membrane Transplantation: A Revolutionary Approach to Healing
What Is Amniotic Membrane Transplantation?
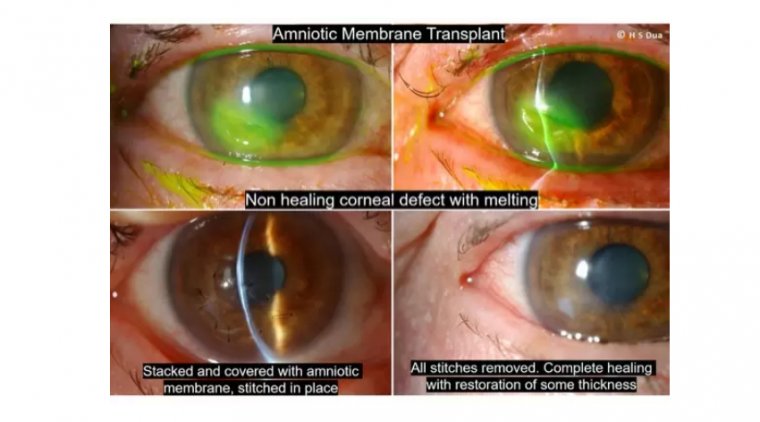
Amniotic membrane transplantation (AMT) is a surgical procedure that involves using the amniotic membrane, which is the innermost layer of the placenta, to treat a variety of ocular, dermatological, and other medical conditions. The amniotic membrane is an attractive biomaterial for transplantation because it is rich in growth factors and cytokines that promote tissue healing. It also has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties.
The amniotic membrane has been used for various medical applications as it promotes tissue healing and reduces inflammation. The most common conditions treated with AMT include:
1. Ocular Surface Disorders: Amniotic membrane transplantation has been used to treat a range of ocular surface disorders, including:
● Conjunctivochalasis
● Pterygium
● Corneal ulcers
● Chemical burns
● Stevens-Johnson syndrome
● Ocular cicatricial pemphigoid
2. Dermatological Conditions: AMT has been used to treat a variety of dermatological conditions, including:
● Burns
● Chronic wounds
● Diabetic foot ulcers
● Pyoderma gangrenosum
● Vitiligo
● Radiation dermatitis
● Eczema
● Psoriasis
3. Other Medical Conditions: AMT has also been used to treat other medical conditions, including:
● Oral and periodontal diseases
● Genitourinary disorders
● Vocal cord scarring
How is Amniotic Membrane Transplantation Performed?
1. Obtain amniotic membrane: Amniotic membrane can be obtained either from a donor placenta immediately after birth (fresh) or from a tissue bank (preserved).
2. Prepare the amniotic membrane: The amniotic membrane is processed and sterilized to remove potential pathogens.
3. Anesthesia: The patient is given either local or general anesthesia, depending on the extent and location of the area to be treated.
4. Amniotic membrane placement: The amniotic membrane is carefully placed onto the affected area, with the epithelial side facing up.
5. Securing the amniotic membrane: The amniotic membrane is secured using sutures, glue, or a contact lens, depending on the transplantation area.
6. Post-operative care: The patient may need to wear an eye patch or bandage over the area of transplantation to protect the membrane and facilitate
.jpg)
The Potential Benefits Of Amniotic Membrane Transplantation
Amniotic membrane transplantation has several potential benefits for patients with various medical conditions, including:
1. Reduces Inflammation: The amniotic membrane contains anti-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors that help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
2. Promotes Tissue Regeneration: The amniotic membrane is rich in growth factors and cytokines that promote the regeneration of damaged tissue, which is particularly useful in treating chronic wounds and ulcers.
3. Pain Relief: AMT has been shown to reduce pain and discomfort associated with certain conditions, such as ocular surface disorders.
4. Low Risk of Rejection: The amniotic membrane is an immunologically privileged tissue, meaning that it does not elicit a significant immune response and has a low risk of rejection.
5. Improved Cosmesis: AMT can help improve the appearance of scars and other skin lesions and also helps prevent the formation of adhesions and scars in surgical wounds.
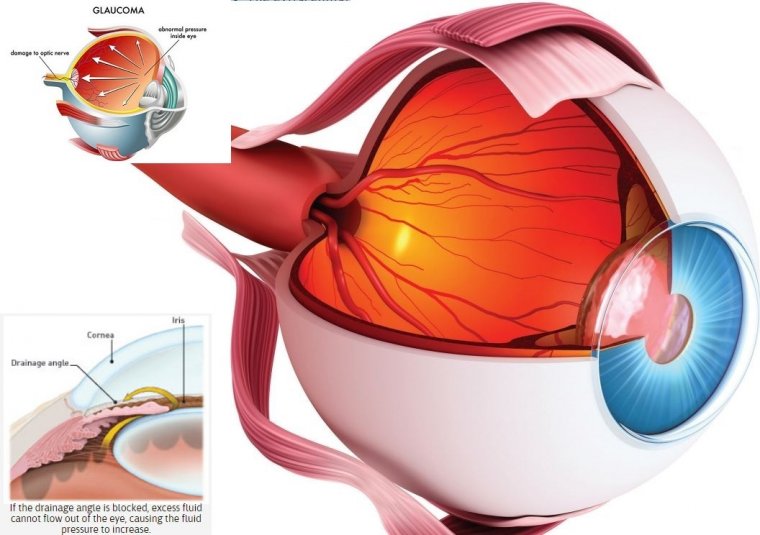
Risks or Complications Associated with Amniotic Membrane Transplantation
1. Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection with AMT. Using contaminated or improperly sterilized instruments during surgery may lead to bacterial or fungal infections. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, pain, and discharge from the eye. Antibiotic drops or ointments are usually prescribed to prevent or treat infections.
2. Inflammation: Inflammation is a common complication of AMT. The immune system may react to the transplanted tissue, causing redness, swelling, and discomfort. Steroid eye drops are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and prevent scarring.
3. Complications with Contact Lens Wear: Patients who undergo AMT may be prescribed contact lenses to help with healing and comfort. However, there is a risk of complications with contact lens wear, including infection, corneal ulcers, and corneal neovascularization. Patients should be monitored closely for any signs of complications and should follow strict hygiene practices when handling their contact lenses.
4. Adverse Reactions to Preservatives: Eye drops and ointments after AMT may contain preservatives that can cause adverse reactions. Preservatives such as benzalkonium chloride can cause dry eye, irritation, and other ocular surface disorders. Patients should inform their ophthalmologist of any allergies or sensitivities to preservatives.
Recovery Process
The recovery process after AMT varies depending on the individual and the condition being treated. Patients are generally advised to avoid rubbing their eyes, engaging in strenuous activities, and exposing their eyes to water or other irritants. Eye drops and ointments are typically prescribed to prevent infection and reduce inflammation.
Patients may experience some discomfort or mild pain after surgery, but this can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain medication or prescription pain relievers. Patients are usually advised to avoid driving or operating heavy machinery for at least 24 hours after surgery.
The length of the recovery period depends on the severity of the condition being treated and the success of the surgery. Some patients may experience complete healing within a few weeks, while others may require several months to recover fully.
Effectiveness of AMT in Treating Various Conditions
AMT is an effective treatment option for various ocular surface disorders. Some of the conditions that can be treated with AMT include:
1. Corneal Ulcers: AMT can help promote healing and reduce scarring in corneal ulcers. The membrane provides a protective barrier over the ulcerated area, allowing the cornea to heal.
2. Chemical Burns: Chemical burns can cause severe damage to the ocular surface. AMT can help to reduce inflammation and promote healing in these cases.
3. Dry Eye Disease: AMT can help to improve the symptoms of dry eye disease by providing a protective layer over the ocular surface and promoting the growth of new tissue
Are There Any Alternatives To Amniotic Membrane Transplantation?
While amniotic membrane transplantation is a beneficial and effective treatment option for many conditions, alternative treatments are available for patients who may not be suitable candidates for this procedure or prefer a different approach. Here are some alternatives to amniotic membrane transplantation:
1. Artificial Tears: Artificial tears are a standard treatment option for patients with dry eye syndrome. They can help lubricate and moisturize the eyes, relieving dryness and discomfort.
2. Autologous Serum Eye Drops: Autologous serum eye drops are a personalized treatment option involving using a patient's blood to create eye drops. These eye drops contain growth factors and other healing properties that can help improve symptoms of dry eye syndrome and other eye conditions.
3. Topical Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that can be applied directly to the eye to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms of conditions such as uveitis and scleritis.
4. Cyclosporine: Cyclosporine is an immunosuppressant medication that can help reduce eye inflammation and improve symptoms of conditions such as dry eye syndrome and uveitis.
5. Punctal Plugs: Punctal plugs are small devices that can be inserted into the tear ducts to help retain moisture in the eyes and improve symptoms of dry eye syndrome.
6. Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be recommended as an alternative to amniotic membrane transplantation. For example, patients with pterygium or corneal scarring may require surgical intervention to improve their vision.
It is important to note that the most appropriate treatment option for each patient depends on their condition, medical history, and other factors. Patients should discuss their treatment options with their healthcare provider to determine the best approach for their needs.
Author: Dr. Muhammad Saad, Resident Ophthalmologist at Alshifa Trust Eye Hospital in Rawalpindi, Pakistan
(1).jpg)