A Comprehensive Guide to Blepharospasm Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Blepharospasm?
Ah, the world of blinking - a wondrous symphony of muscles, nerves, and reflexes that keep our eyes moist and protected. But what happens when your eyelids go rogue and dance to their beat? Enter Blepharospasm: the uninvited party crasher of the ocular realm.
Blepharospasm is characterized by the involuntary contraction of eyelid muscles, causing abnormal and excessive blinking. Don't let its fancy name fool you, though; it's estimated that about 5 in 100,000 people worldwide are affected by this unwelcome eyelid jig.
Types and Causes of Blepharospasm
Blepharospasm manifests itself in two distinct forms:
1. Primary Blepharospasm: This form has no identifiable underlying cause, akin to an unexpected guest whose arrival cannot be attributed to any particular source.
2. Secondary Blepharospasm: This variation is triggered by other medical conditions or medications, making it a meaningful outcome rather than the primary issue.
While the exact cause of Blepharospasm remains unknown, research has identified several genetic and environmental factors that may play a role in its development:
1. Genetic factors: Some studies have suggested that there may be a genetic component to Blepharospasm. Individuals with a family history of the condition or other movement disorders might be more likely to develop it. However, the precise genetic mechanisms and specific genes involved have yet to elucidate fully.
2. Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as stress, bright lights, air pollution, or allergens, may trigger or exacerbate Blepharospasm symptoms. These factors can irritate the eyes or lead to increased sensitivity, potentially contributing to the onset or worsening of the condition.
3. Age and sex: Blepharospasm is more commonly observed in middle-aged and older adults, affecting women more frequently than men. This suggests that age and sex may play a role in the development of the condition. However, the reasons for these differences still need to be clarified.
4. Underlying medical conditions: In some cases, blepharospasm may be secondary to other medical conditions, such as Parkinson's disease, Meige syndrome, or dystonia. These conditions can cause abnormalities in the neurological pathways responsible for muscle control, leading to involuntary contractions in the eyelids and other facial muscles.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Blepharospasm is characterized by a range of distinct symptoms that can significantly impact an individual's daily life:
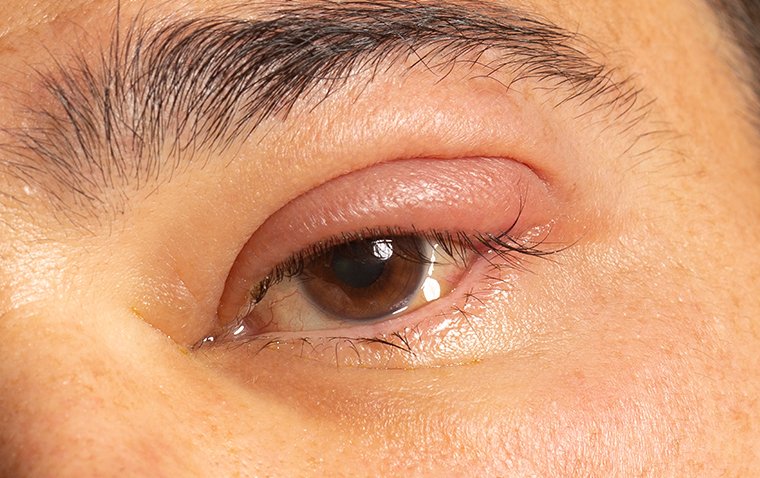
● Involuntary contractions of the eyelid muscles: Patients with blepharospasm experience involuntary contractions of the orbicularis oculi muscle, which controls the eyelids. These contractions cause the eyelids to twitch and flutter unpredictably, often without any discernible pattern or warning.
● Extension of tics, twitches, or spasms to other facial muscles: In some instances, blepharospasm may not be limited to the eyelids. It can also involve other facial muscles, leading to involuntary movements and contractions in various regions of the face. This can result in additional discomfort and challenges for the affected individual.
● Impact on vision and quality of life: Blepharospasm's continuous and uncontrolled nature can significantly affect a person's vision and overall quality of life. The constant blinking and eyelid spasms may interfere with daily activities such as reading, driving, working, and social interactions. Furthermore, the condition can lead to eye irritation, dryness, or even corneal damage due to excessive blinking or forced eyelid closure.
Fortunately, a qualified ophthalmologist can diagnose blepharospasm through a comprehensive examination and expert assessment.
The examination and diagnosis of blepharospasm involve a series of steps conducted by an ophthalmologist or a neurologist to evaluate the patient's symptoms and determine the appropriate course of action. These steps typically include the following:
1. Medical history and symptom assessment: The healthcare professional will inquire about the patient's medical history, the onset of symptoms, and any potential triggers or exacerbating factors. This information helps to identify possible underlying causes and distinguish between primary and secondary Blepharospasm.
2. Physical examination: A thorough biological study will focus on the patient's eyes and surrounding facial muscles. The doctor will assess the frequency and intensity of eyelid contractions, observe any abnormalities in eye movement, and evaluate the presence of other facial muscle involvement.
3. Neurological examination: To rule out potential neurological disorders, the healthcare professional may conduct a neurological exam, including tests for muscle strength, reflexes, coordination, and sensation.
4. Ophthalmic examination: An ophthalmologist will perform a comprehensive eye exam to evaluate the overall health of the patient's eyes. This examination may include tests for visual acuity, eye pressure, and eye alignment, as well as a thorough assessment of the ocular surface and retina.
5. Additional tests and imaging: Further tests or imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans may be necessary to rule out other conditions causing the symptoms. Blood tests might also be performed to assess for potential underlying systemic diseases.
6. Differential diagnosis: The healthcare professional will consider other potential causes of the patient's symptoms, such as hemifacial spasms, tic disorders, or other movement disorders. This differential diagnosis process helps to confirm the presence of blepharospasm and exclude other possible conditions.
Once the examination and diagnostic process are complete, the doctor will discuss the findings with the patient and recommend an appropriate treatment plan to effectively manage the symptoms of blepharospasm.
Treatment Options
A range of treatment options exists to manage and alleviate the symptoms of blepharospasm effectively:
● Botulinum toxin injections: One of the most common and effective treatments for blepharospasm, botulinum toxin injections work by temporarily weakening the overactive muscles responsible for eyelid contractions. This reduces the frequency and severity of involuntary blinking and spasms, providing patients with significant relief.
● Oral medications: In some cases, doctors may prescribe oral medications such as anticholinergics, benzodiazepines, or muscle relaxants to help alleviate muscle spasms and restore normal function to the affected eyelids. The choice of medication depends on the patient's symptoms, medical history, and response to treatment.
● Surgery: For patients who do not respond adequately to botulinum toxin injections or oral medications, a surgical procedure called myectomy may be considered. This involves removing or deactivating the affected muscles, reducing the involuntary contractions and providing relief from Blepharospasm. Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases when other treatment options have proven ineffective.
● Complementary therapies: In conjunction with conventional treatments, some patients may benefit from complementary therapies such as biofeedback, yoga, or acupuncture. These approaches can help individuals regain control over their affected eyelids, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. Discussing complementary therapies with a healthcare professional to ensure their safety and effectiveness in managing Blepharospasm symptoms is essential.
.gif)
Complications and Prognosis
If blepharospasm is not addressed and treated, it may give rise to further complications:
● Potential complications: Untreated or inadequately managed blepharospasm can have several consequences. Vision impairment may occur due to constant blinking or forced eyelid closure, interfering with normal visual function. Additionally, the condition can lead to social anxiety as individuals may feel self-conscious about their involuntary eye movements, potentially affecting their interpersonal relationships and participation in social activities. Furthermore, the persistent nature of the disorder can cause difficulties in performing daily tasks, such as reading, driving, and working, which may reduce the overall quality of life.
On the other hand, with appropriate treatment and management:
● Prognosis and expected outcomes: Most individuals affected by blepharospasm can attain significant symptom relief, considerably improving their quality of life. By addressing involuntary muscle contractions, patients can regain control over their eyelids and restore normal visual function, allowing them to engage in daily activities without hindrance. With timely and effective treatment, individuals can expect to live a life that is no longer burdened by uncontrollable eyelid movements.
Conclusion
To recap, blepharospasm is an involuntary blinking disorder that can have various causes and impacts on your life. But with the proper treatment and perseverance, you can show blepharospasm the door.
If you're experiencing symptoms of blepharospasm, don't hesitate to seek medical help. Your ophthalmologist is standing by, ready to help you regain control of your eyelids and restore harmony to your blinking world.
Remember, it's always better to face the music and deal with the blinking' problem rather than let it steal the show. So, schedule that appointment and put the spotlight back on your healthy eyes where it belongs. Together, you and your eye doctor can kick blepharospasm out of the party for good and enjoy the beauty of a well-timed blink!
FAQ
The exact cause of blepharospasm is unknown, but it is believed to be related to abnormal functioning of the basal ganglia, a group of cells in the brain that help control movement.
(1).jpg)